Code-DKT: A Code-based Knowledge Tracing Model for Programming Tasks
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2022
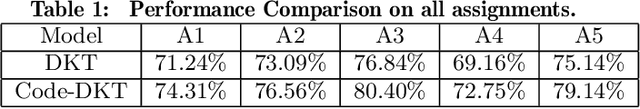
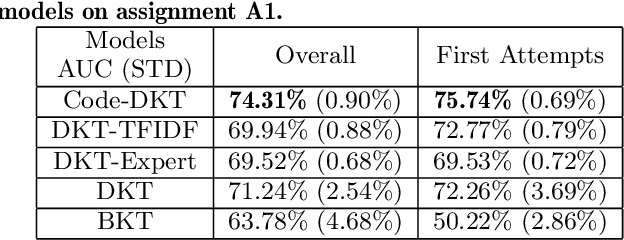
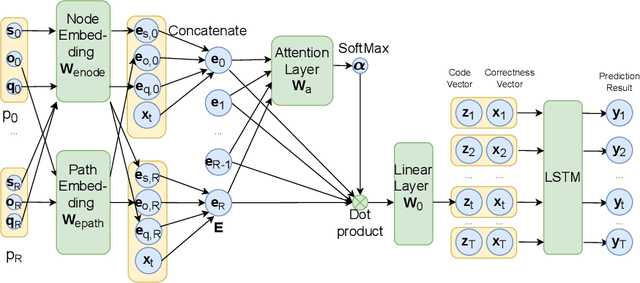
Knowledge tracing (KT) models are a popular approach for predicting students' future performance at practice problems using their prior attempts. Though many innovations have been made in KT, most models including the state-of-the-art Deep KT (DKT) mainly leverage each student's response either as correct or incorrect, ignoring its content. In this work, we propose Code-based Deep Knowledge Tracing (Code-DKT), a model that uses an attention mechanism to automatically extract and select domain-specific code features to extend DKT. We compared the effectiveness of Code-DKT against Bayesian and Deep Knowledge Tracing (BKT and DKT) on a dataset from a class of 50 students attempting to solve 5 introductory programming assignments. Our results show that Code-DKT consistently outperforms DKT by 3.07-4.00% AUC across the 5 assignments, a comparable improvement to other state-of-the-art domain-general KT models over DKT. Finally, we analyze problem-specific performance through a set of case studies for one assignment to demonstrate when and how code features improve Code-DKT's predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge