Co-training for Policy Learning
Paper and Code
Jul 03, 2019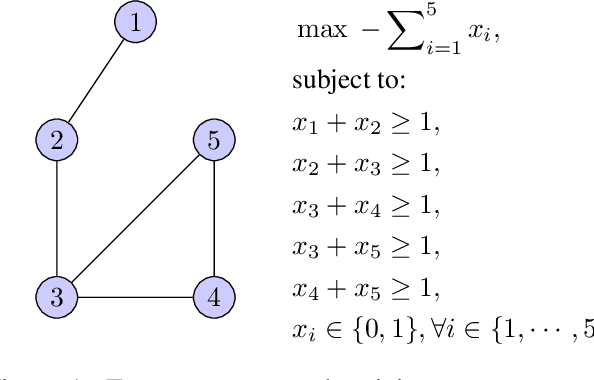
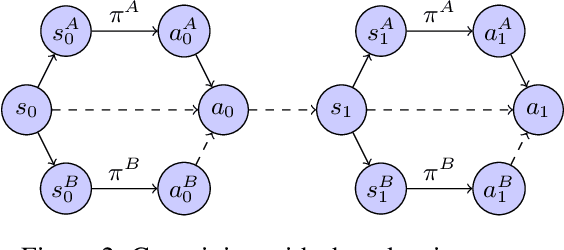
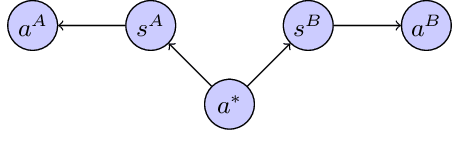
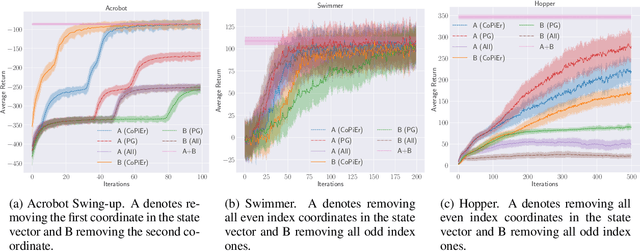
We study the problem of learning sequential decision-making policies in settings with multiple state-action representations. Such settings naturally arise in many domains, such as planning (e.g., multiple integer programming formulations) and various combinatorial optimization problems (e.g., those with both integer programming and graph-based formulations). Inspired by the classical co-training framework for classification, we study the problem of co-training for policy learning. We present sufficient conditions under which learning from two views can improve upon learning from a single view alone. Motivated by these theoretical insights, we present a meta-algorithm for co-training for sequential decision making. Our framework is compatible with both reinforcement learning and imitation learning. We validate the effectiveness of our approach across a wide range of tasks, including discrete/continuous control and combinatorial optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge