Circumventing Outliers of AutoAugment with Knowledge Distillation
Paper and Code
Mar 25, 2020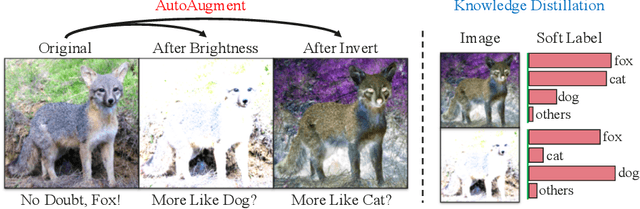
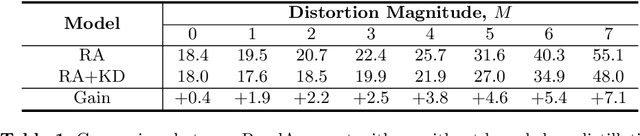
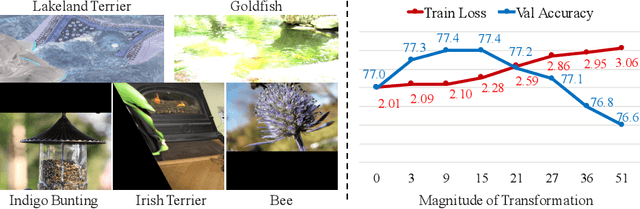
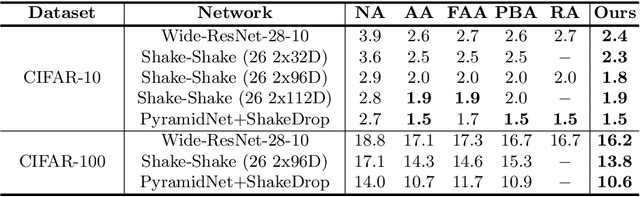
AutoAugment has been a powerful algorithm that improves the accuracy of many vision tasks, yet it is sensitive to the operator space as well as hyper-parameters, and an improper setting may degenerate network optimization. This paper delves deep into the working mechanism, and reveals that AutoAugment may remove part of discriminative information from the training image and so insisting on the ground-truth label is no longer the best option. To relieve the inaccuracy of supervision, we make use of knowledge distillation that refers to the output of a teacher model to guide network training. Experiments are performed in standard image classification benchmarks, and demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in suppressing noise of data augmentation and stabilizing training. Upon the cooperation of knowledge distillation and AutoAugment, we claim the new state-of-the-art on ImageNet classification with a top-1 accuracy of 85.8%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge