CGS-Net: Aggregating Colour, Geometry and Semantic Features for Large-Scale Indoor Place Recognition
Paper and Code
Feb 04, 2022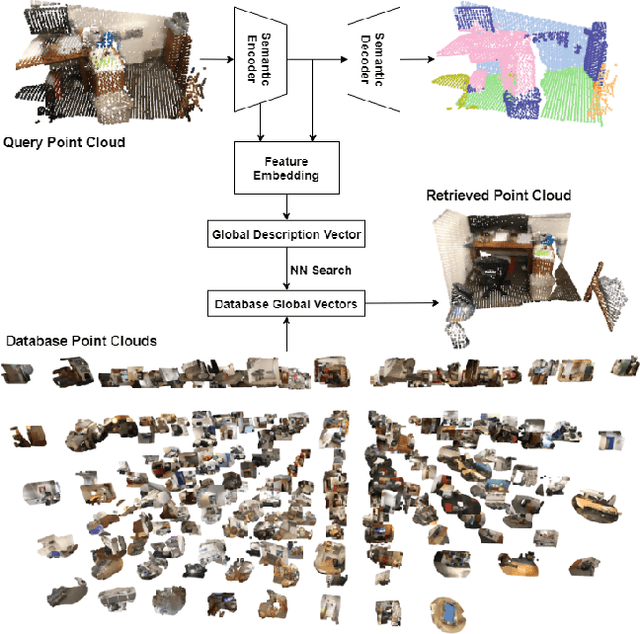
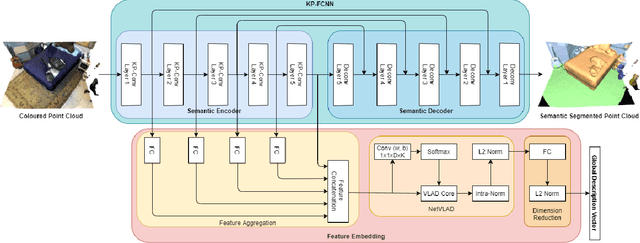
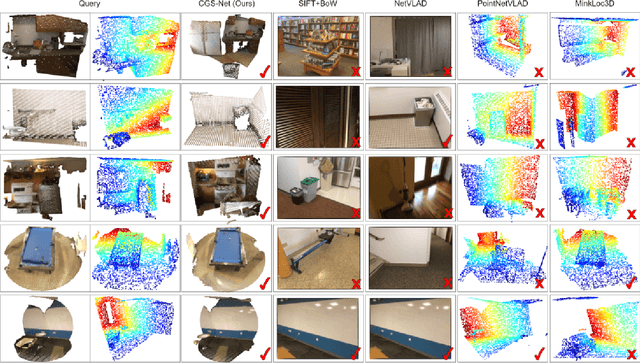
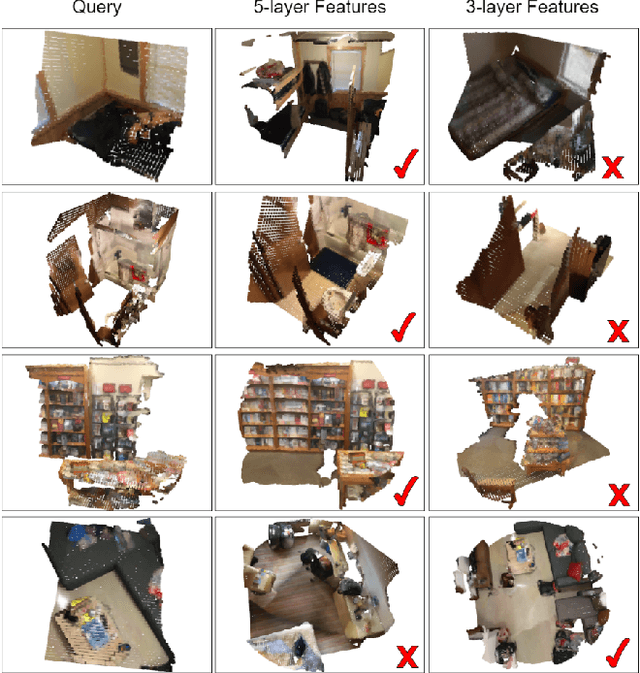
We describe an approach to large-scale indoor place recognition that aggregates low-level colour and geometric features with high-level semantic features. We use a deep learning network that takes in RGB point clouds and extracts local features with five 3-D kernel point convolutional (KPConv) layers. We specifically train the KPConv layers on the semantic segmentation task to ensure that the extracted local features are semantically meaningful. Then, feature maps from all the five KPConv layers are concatenated together and fed into the NetVLAD layer to generate the global descriptors. The approach is trained and evaluated using a large-scale indoor place recognition dataset derived from the ScanNet dataset, with a test set comprising 3,608 point clouds generated from 100 different rooms. Comparison with a traditional feature based method and three state-of-the-art deep learning methods demonstrate that the approach significantly outperforms all four methods, achieving, for example, a top-3 average recall rate of 75% compared with 41% for the closest rival method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge