Cephalogram Synthesis and Landmark Detection in Dental Cone-Beam CT Systems
Paper and Code
Sep 09, 2020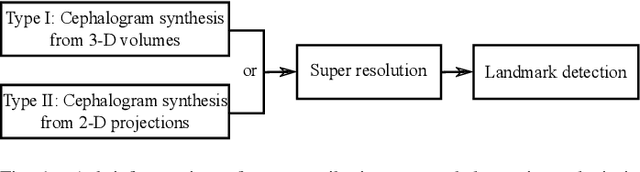
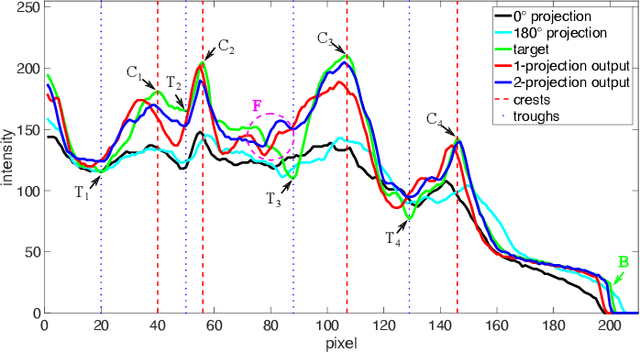
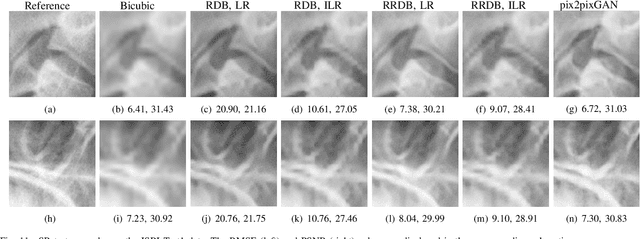
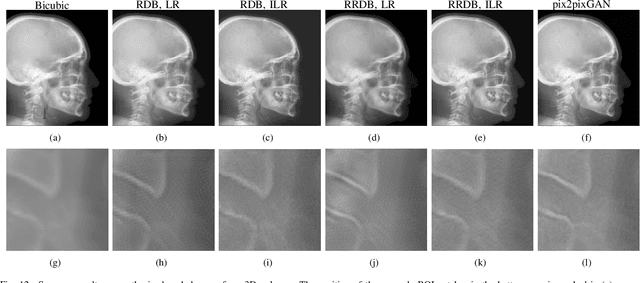
Due to the lack of standardized 3D cephalometric analytic methodology, 2D cephalograms synthesized from 3D cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) volumes are widely used for cephalometric analysis in dental CBCT systems. However, compared with conventional X-ray film based cephalograms, such synthetic cephalograms lack image contrast and resolution. In addition, the radiation dose during the scan for 3D reconstruction causes potential health risks. In this work, we propose a sigmoid-based intensity transform that uses the nonlinear optical property of X-ray films to increase image contrast of synthetic cephalograms. To improve image resolution, super resolution deep learning techniques are investigated. For low dose purpose, the pixel-to-pixel generative adversarial network (pix2pixGAN) is proposed for 2D cephalogram synthesis directly from two CBCT projections. For landmark detection in the synthetic cephalograms, an efficient automatic landmark detection method using the combination of LeNet-5 and ResNet50 is proposed. Our experiments demonstrate the efficacy of pix2pixGAN in 2D cephalogram synthesis, achieving an average peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) value of 33.8 with reference to the cephalograms synthesized from 3D CBCT volumes. Pix2pixGAN also achieves the best performance in super resolution, achieving an average PSNR value of 32.5 without the introduction of checkerboard or jagging artifacts. Our proposed automatic landmark detection method achieves 86.7% successful detection rate in the 2 mm clinical acceptable range on the ISBI Test1 data, which is comparable to the state-of-the-art methods. The method trained on conventional cephalograms can be directly applied to landmark detection in the synthetic cephalograms, achieving 93.0% and 80.7% successful detection rate in 4 mm precision range for synthetic cephalograms from 3D volumes and 2D projections respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge