Bridging Physics-based and Data-driven modeling for Learning Dynamical Systems
Paper and Code
Nov 20, 2020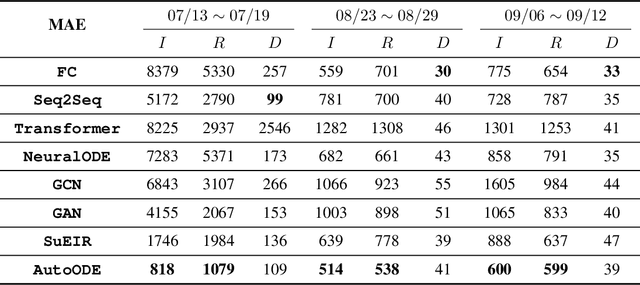
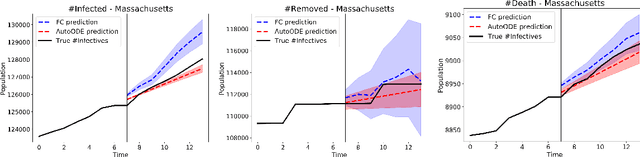
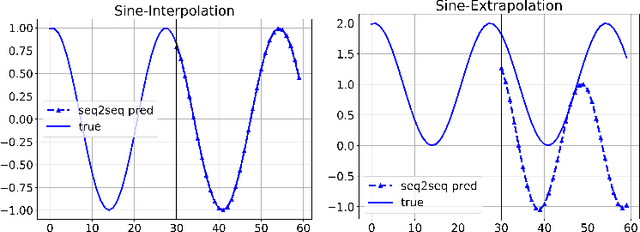
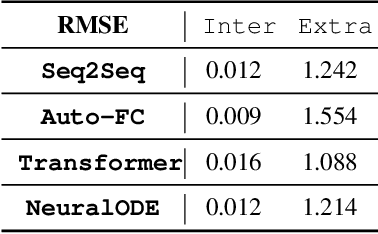
How can we learn a dynamical system to make forecasts, when some variables are unobserved? For instance, in COVID-19, we want to forecast the number of infected and death cases but we do not know the count of susceptible and exposed people. While mechanics compartment models are widely-used in epidemic modeling, data-driven models are emerging for disease forecasting. As a case study, we compare these two types of models for COVID-19 forecasting and notice that physics-based models significantly outperform deep learning models. We present a hybrid approach, AutoODE-COVID, which combines a novel compartmental model with automatic differentiation. Our method obtains a 57.4% reduction in mean absolute errors for 7-day ahead COVID-19 forecasting compared with the best deep learning competitor. To understand the inferior performance of deep learning, we investigate the generalization problem in forecasting. Through systematic experiments, we found that deep learning models fail to forecast under shifted distributions either in the data domain or the parameter domain. This calls attention to rethink generalization especially for learning dynamical systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge