Bounding Reconstruction Attack Success of Adversaries Without Data Priors
Paper and Code
Feb 20, 2024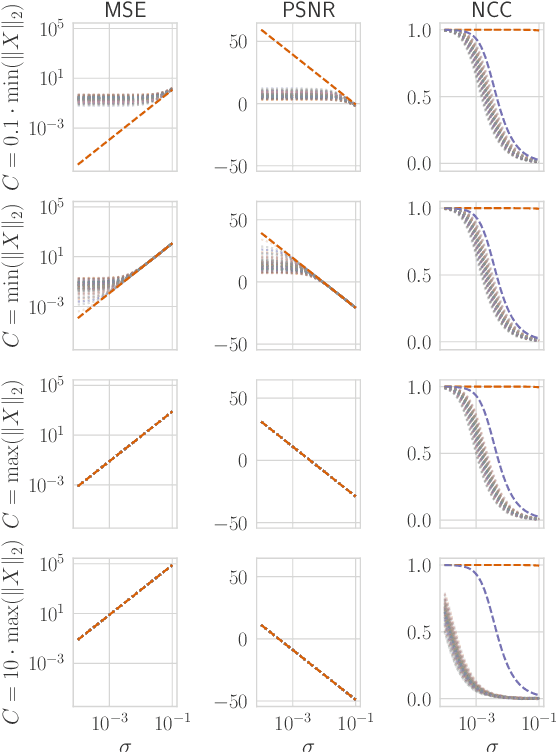
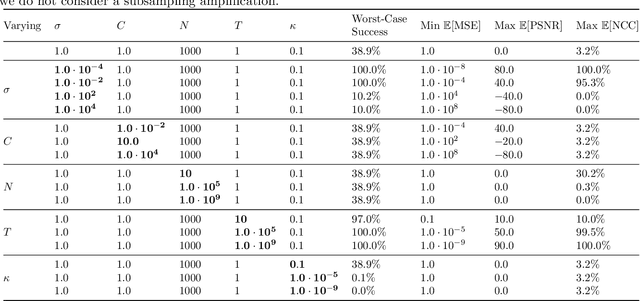
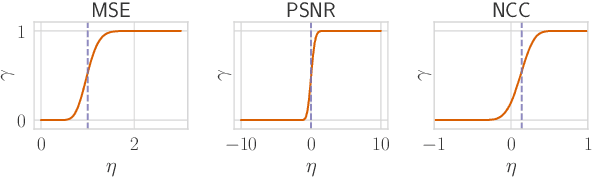
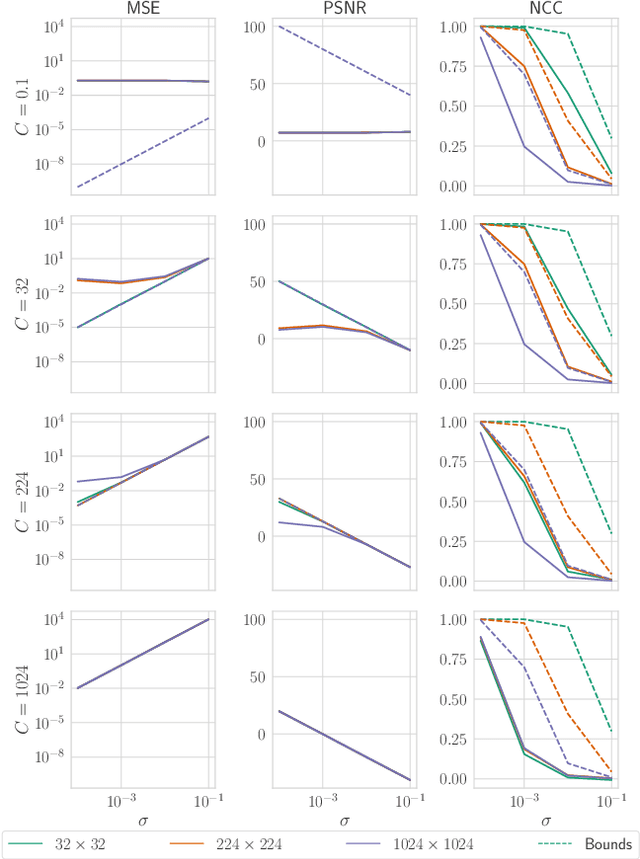
Reconstruction attacks on machine learning (ML) models pose a strong risk of leakage of sensitive data. In specific contexts, an adversary can (almost) perfectly reconstruct training data samples from a trained model using the model's gradients. When training ML models with differential privacy (DP), formal upper bounds on the success of such reconstruction attacks can be provided. So far, these bounds have been formulated under worst-case assumptions that might not hold high realistic practicality. In this work, we provide formal upper bounds on reconstruction success under realistic adversarial settings against ML models trained with DP and support these bounds with empirical results. With this, we show that in realistic scenarios, (a) the expected reconstruction success can be bounded appropriately in different contexts and by different metrics, which (b) allows for a more educated choice of a privacy parameter.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge