Bias Mitigation of Face Recognition Models Through Calibration
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2021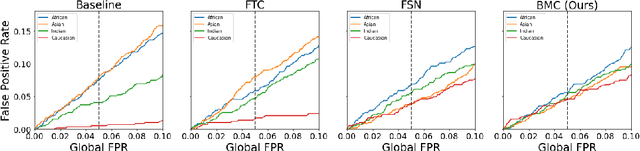

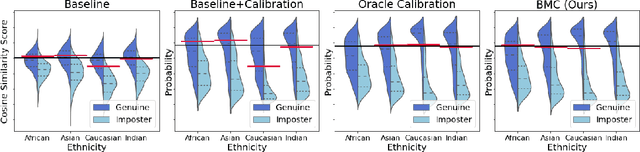
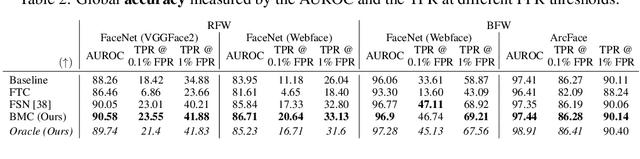
Face recognition models suffer from bias: for example, the probability of a false positive (incorrect face match) strongly depends on sensitive attributes like ethnicity. As a result, these models may disproportionately and negatively impact minority groups when used in law enforcement. In this work, we introduce the Bias Mitigation Calibration (BMC) method, which (i) increases model accuracy (improving the state-of-the-art), (ii) produces fairly-calibrated probabilities, (iii) significantly reduces the gap in the false positive rates, and (iv) does not require knowledge of the sensitive attribute.
* 22 pages, 20 tables, 13 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge