Belief dynamics extraction
Paper and Code
Feb 02, 2019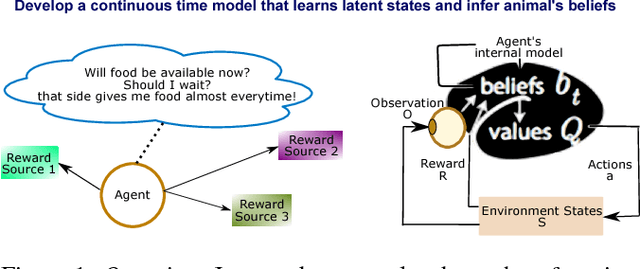
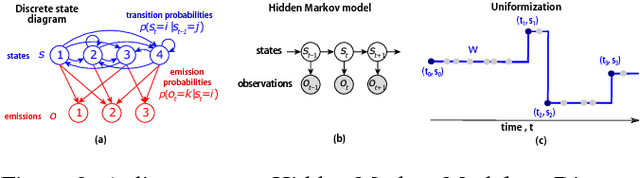
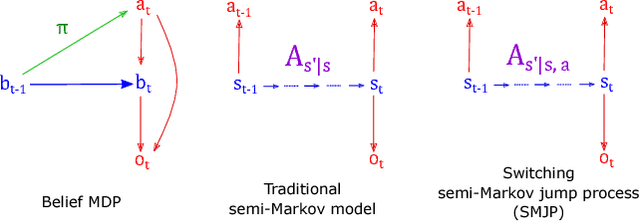
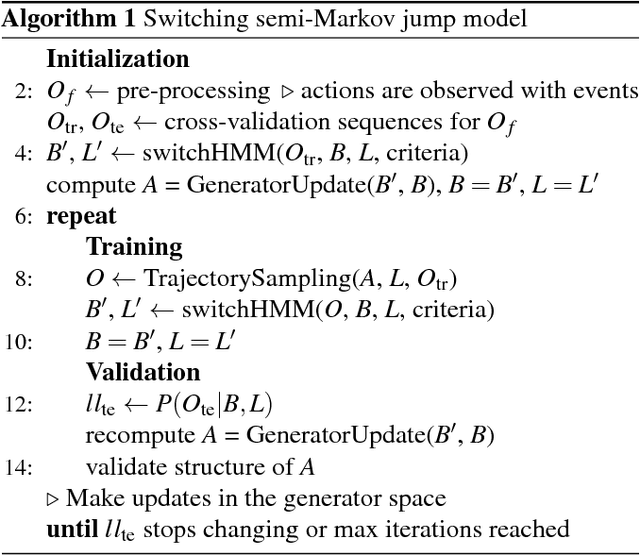
Animal behavior is not driven simply by its current observations, but is strongly influenced by internal states. Estimating the structure of these internal states is crucial for understanding the neural basis of behavior. In principle, internal states can be estimated by inverting behavior models, as in inverse model-based Reinforcement Learning. However, this requires careful parameterization and risks model-mismatch to the animal. Here we take a data-driven approach to infer latent states directly from observations of behavior, using a partially observable switching semi-Markov process. This process has two elements critical for capturing animal behavior: it captures non-exponential distribution of times between observations, and transitions between latent states depend on the animal's actions, features that require more complex non-markovian models to represent. To demonstrate the utility of our approach, we apply it to the observations of a simulated optimal agent performing a foraging task, and find that latent dynamics extracted by the model has correspondences with the belief dynamics of the agent. Finally, we apply our model to identify latent states in the behaviors of monkey performing a foraging task, and find clusters of latent states that identify periods of time consistent with expectant waiting. This data-driven behavioral model will be valuable for inferring latent cognitive states, and thereby for measuring neural representations of those states.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge