Behavioral Intention Prediction in Driving Scenes: A Survey
Paper and Code
Nov 02, 2022

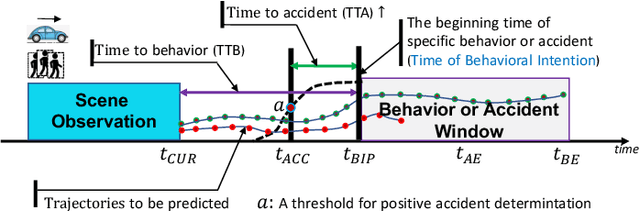

In the driving scene, the road participants usually show frequent interaction and intention understanding with the surrounding. Ego-agent (each road participant itself) conducts the prediction of what behavior will be done by other road users all the time and expects a shared and consistent understanding. For instance, we need to predict the next movement of other road users and expect a consistent joint action to avoid unexpected accident. Behavioral Intention Prediction (BIP) is to simulate such a human consideration process and fulfill the beginning time prediction of specific behaviors. It provides an earlier signal promptly than the specific behaviors for whether the surrounding road participants will present specific behavior (crossing, overtaking, and turning, etc.) in near future or not. More and more works in BIP are based on deep learning models to take advantage of big data, and focus on developing effective inference approaches (e.g., explainable inference, cross-modality fusion, and simulation augmentation). Therefore, in this work, we focus on BIP-conditioned prediction tasks, including trajectory prediction, behavior prediction, and accident prediction and explore the differences among various works in this field. Based on this investigation and the findings, we discuss the open problems in behavioral intention prediction and propose future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge