Auxiliary Sequence Labeling Tasks for Disfluency Detection
Paper and Code
Oct 24, 2020
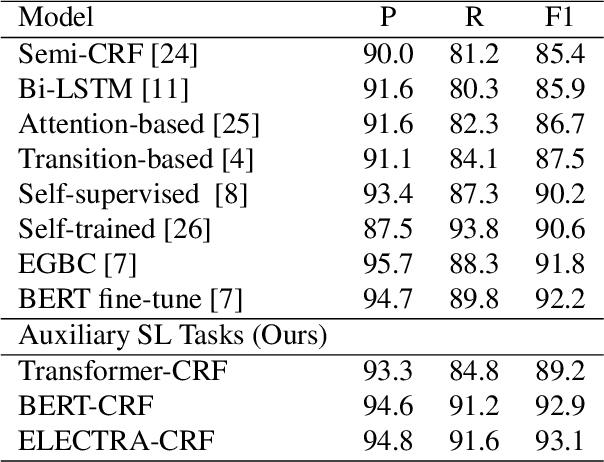
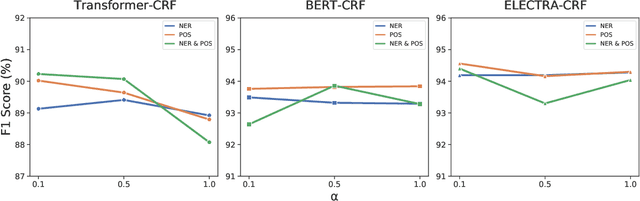
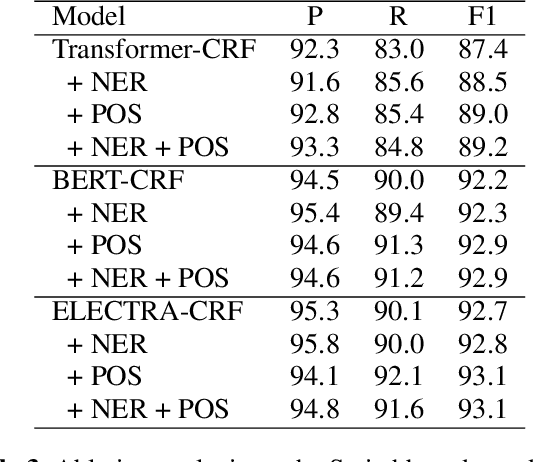
Detecting disfluencies in spontaneous speech is an important preprocessing step in natural language processing and speech recognition applications. In this paper, we propose a method utilizing named entity recognition (NER) and part-of-speech (POS) as auxiliary sequence labeling (SL) tasks for disfluency detection. First, we show that training a disfluency detection model with auxiliary SL tasks can improve its F-score in disfluency detection. Then, we analyze which auxiliary SL tasks are influential depending on baseline models. Experimental results on the widely used English Switchboard dataset show that our method outperforms the previous state-of-the-art in disfluency detection.
* 5 pages, 3 figures, 3 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge