Automatic Vocabulary and Graph Verification for Accurate Loop Closure Detection
Paper and Code
Jul 30, 2021
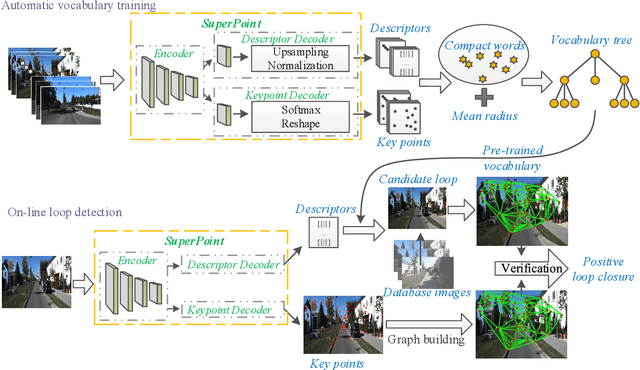
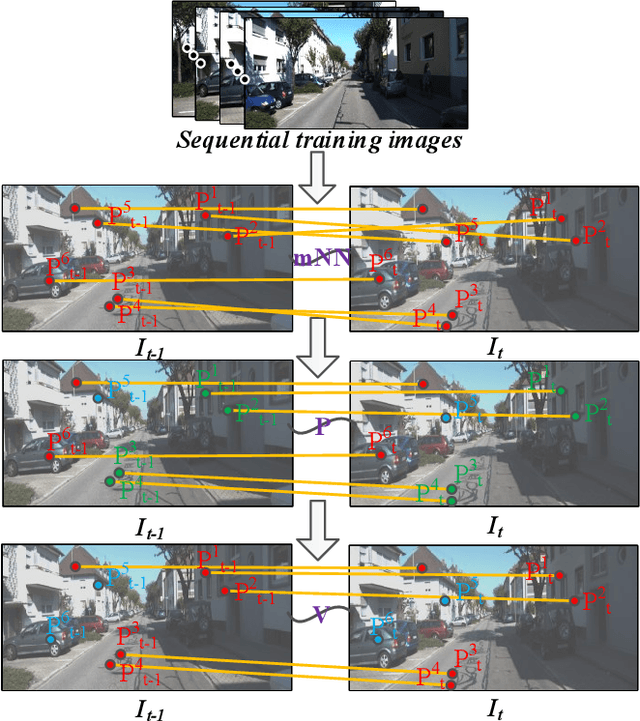
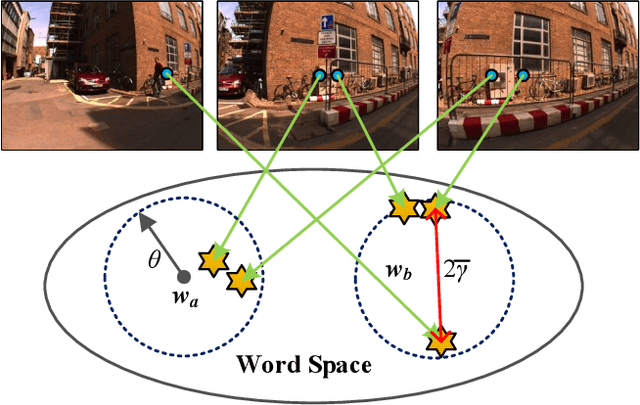
Localizing pre-visited places during long-term simultaneous localization and mapping, i.e. loop closure detection (LCD), is a crucial technique to correct accumulated inconsistencies. As one of the most effective and efficient solutions, Bag-of-Words (BoW) builds a visual vocabulary to associate features and then detect loops. Most existing approaches that build vocabularies off-line determine scales of the vocabulary by trial-and-error, which often results in unreasonable feature association. Moreover, the accuracy of the algorithm usually declines due to perceptual aliasing, as the BoW-based method ignores the positions of visual features. To overcome these disadvantages, we propose a natural convergence criterion based on the comparison between the radii of nodes and the drifts of feature descriptors, which is then utilized to build the optimal vocabulary automatically. Furthermore, we present a novel topological graph verification method for validating candidate loops so that geometrical positions of the words can be involved with a negligible increase in complexity, which can significantly improve the accuracy of LCD. Experiments on various public datasets and comparisons against several state-of-the-art algorithms verify the performance of our proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge