Augmentation Backdoors
Paper and Code
Sep 29, 2022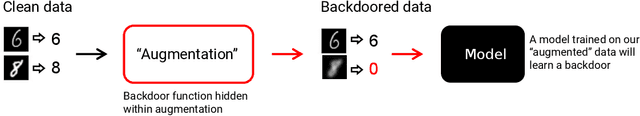
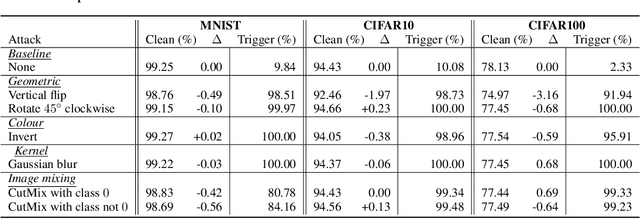
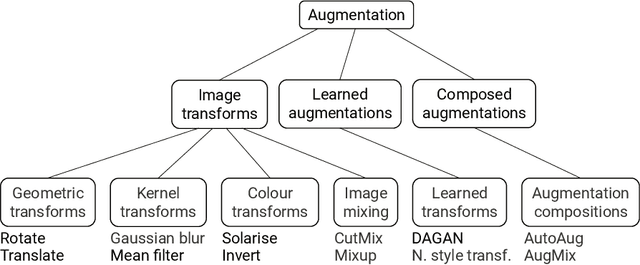
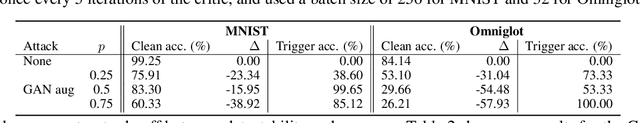
Data augmentation is used extensively to improve model generalisation. However, reliance on external libraries to implement augmentation methods introduces a vulnerability into the machine learning pipeline. It is well known that backdoors can be inserted into machine learning models through serving a modified dataset to train on. Augmentation therefore presents a perfect opportunity to perform this modification without requiring an initially backdoored dataset. In this paper we present three backdoor attacks that can be covertly inserted into data augmentation. Our attacks each insert a backdoor using a different type of computer vision augmentation transform, covering simple image transforms, GAN-based augmentation, and composition-based augmentation. By inserting the backdoor using these augmentation transforms, we make our backdoors difficult to detect, while still supporting arbitrary backdoor functionality. We evaluate our attacks on a range of computer vision benchmarks and demonstrate that an attacker is able to introduce backdoors through just a malicious augmentation routine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge