Attentive Temporal Pooling for Conformer-based Streaming Language Identification in Long-form Speech
Paper and Code
Mar 21, 2022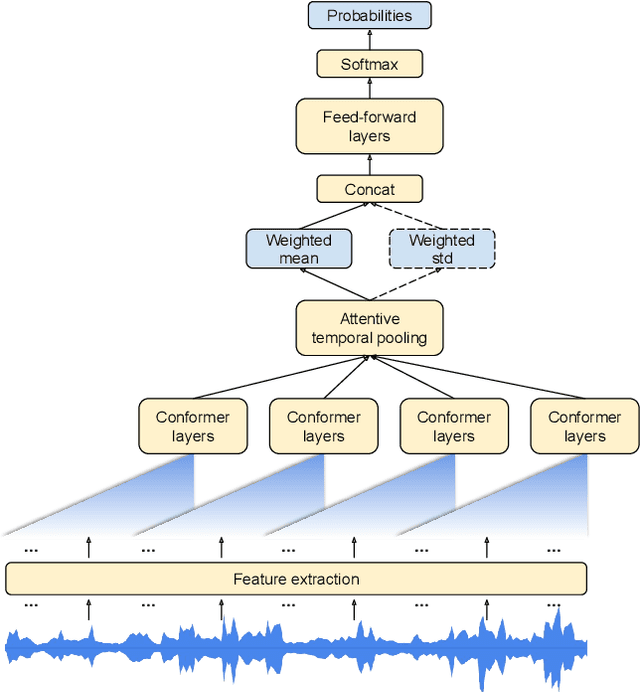
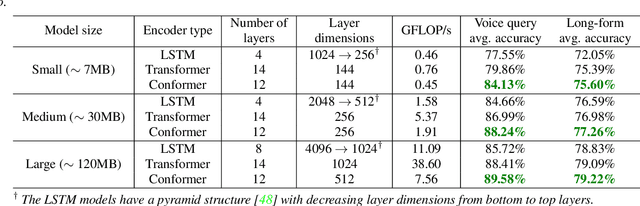
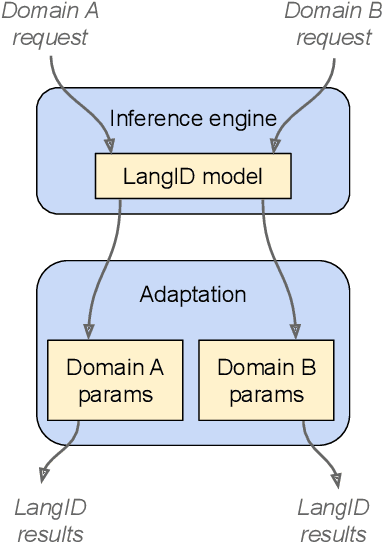
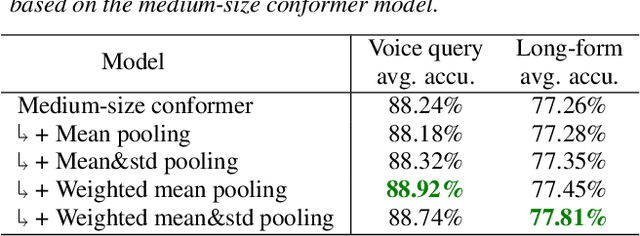
In this paper, we introduce a novel language identification system based on conformer layers. We propose an attentive temporal pooling mechanism to allow the model to carry information in long-form audio via a recurrent form, such that the inference can be performed in a streaming fashion. Additionally, a simple domain adaptation mechanism is introduced to allow adapting an existing language identification model to a new domain where the prior language distribution is different. We perform a comparative study of different model topologies under different constraints of model size, and find that conformer-base models outperform LSTM and transformer based models. Our experiments also show that attentive temporal pooling and domain adaptation significantly improve the model accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge