Asymmetric Similarity Loss Function to Balance Precision and Recall in Highly Unbalanced Deep Medical Image Segmentation
Paper and Code
Jun 29, 2018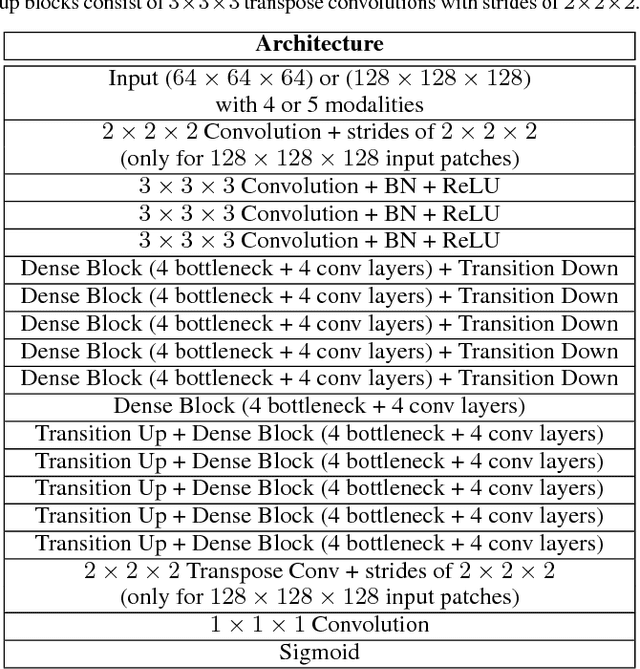
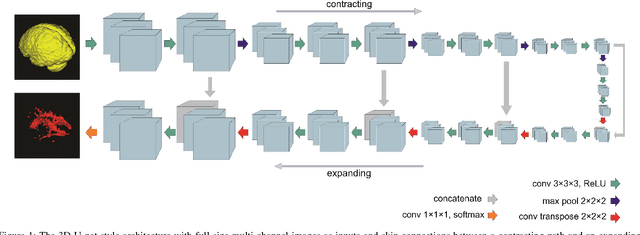
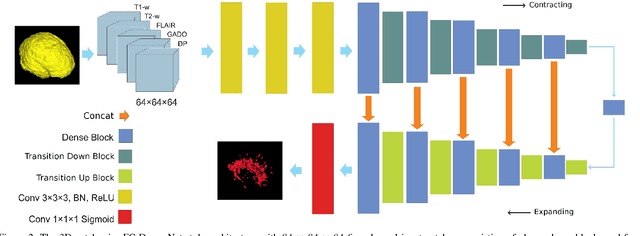
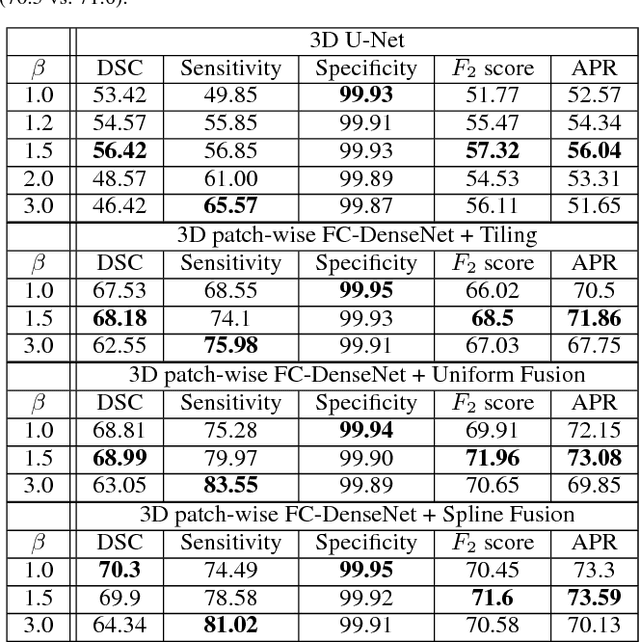
Fully convolutional deep neural networks have been asserted to be fast and precise frameworks with great potential in image segmentation. One of the major challenges in utilizing such networks raises when data is unbalanced, which is common in many medical imaging applications such as lesion segmentation where lesion class voxels are often much lower in numbers than non-lesion voxels. A trained network with unbalanced data may make predictions with high precision and low recall, being severely biased towards the non-lesion class which is particularly undesired in medical applications where false negatives are actually more important than false positives. Various methods have been proposed to address this problem including two step training, sample re-weighting, balanced sampling, and similarity loss functions. In this paper we developed a patch-wise 3D densely connected network with an asymmetric loss function, where we used large overlapping image patches for intrinsic and extrinsic data augmentation, a patch selection algorithm, and a patch prediction fusion strategy based on B-spline weighted soft voting to take into account the uncertainty of prediction in patch borders. We applied this method to lesion segmentation based on the MSSEG 2016 and ISBI 2015 challenges, where we achieved average Dice similarity coefficient of 69.9% and 65.74%, respectively. In addition to the proposed loss, we trained our network with focal and generalized Dice loss functions. Significant improvement in $F_1$ and $F_2$ scores and the APR curve was achieved in test using the asymmetric similarity loss layer and our 3D patch prediction fusion. The asymmetric similarity loss based on $F_\beta$ scores generalizes the Dice similarity coefficient and can be effectively used with the patch-wise strategy developed here to train fully convolutional deep neural networks for highly unbalanced image segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge