AS-Net: Fast Photoacoustic Reconstruction with Multi-feature Fusion from Sparse Data
Paper and Code
Jan 22, 2021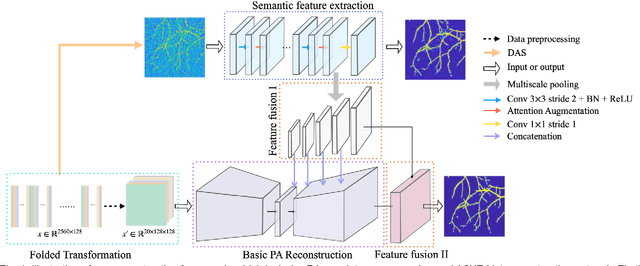
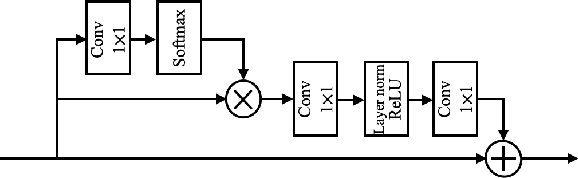
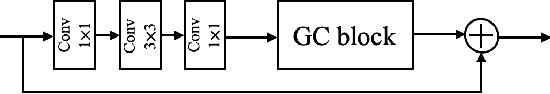
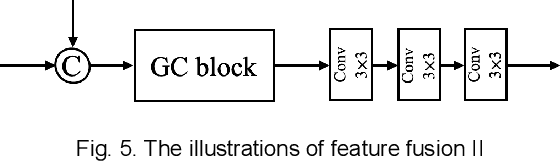
Photoacoustic (PA) imaging is a biomedical imaging modality capable of acquiring high contrast images of optical absorption at depths much greater than traditional optical imaging techniques. However, practical instrumentation and geometry limit the number of available acoustic sensors surrounding the imaging target, which results in sparsity of sensor data. Conventional PA image reconstruction methods give severe artifacts when they are applied directly to these sparse data. In this paper, we first employ a novel signal processing method to make sparse PA raw data more suitable for the neural network, and concurrently speeding up image reconstruction. Then we propose Attention Steered Network (AS-Net) for PA reconstruction with multi-feature fusion. AS-Net is validated on different datasets, including simulated photoacoustic data from fundus vasculature phantoms and real data from in vivo fish and mice imaging experiments. Notably, the method is also able to eliminate some artifacts present in the ground-truth for in vivo data. Results demonstrated that our method provides superior reconstructions at a faster speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge