AS-IntroVAE: Adversarial Similarity Distance Makes Robust IntroVAE
Paper and Code
Jun 28, 2022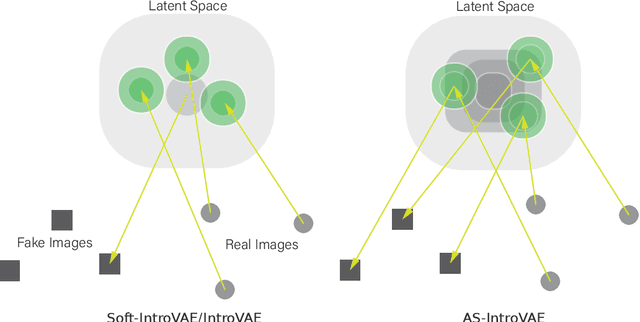
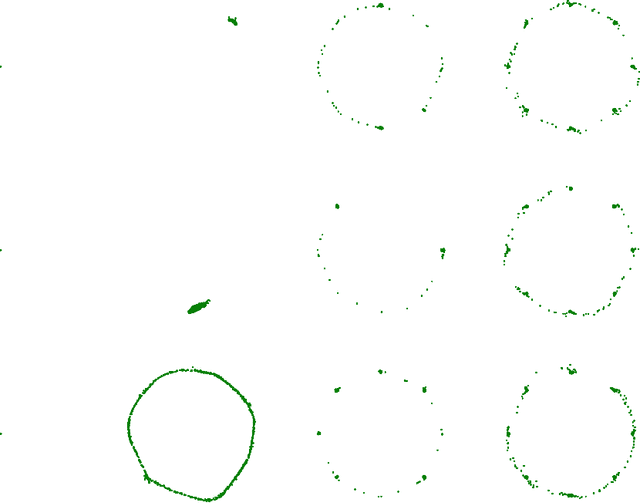
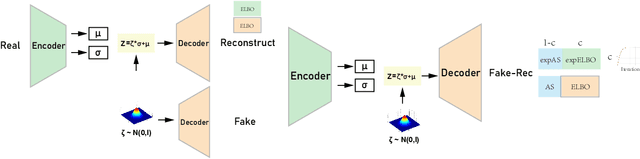
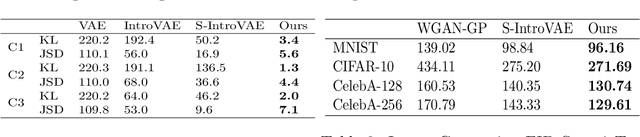

Recently, introspective models like IntroVAE and S-IntroVAE have excelled in image generation and reconstruction tasks. The principal characteristic of introspective models is the adversarial learning of VAE, where the encoder attempts to distinguish between the real and the fake (i.e., synthesized) images. However, due to the unavailability of an effective metric to evaluate the difference between the real and the fake images, the posterior collapse and the vanishing gradient problem still exist, reducing the fidelity of the synthesized images. In this paper, we propose a new variation of IntroVAE called Adversarial Similarity Distance Introspective Variational Autoencoder (AS-IntroVAE). We theoretically analyze the vanishing gradient problem and construct a new Adversarial Similarity Distance (AS-Distance) using the 2-Wasserstein distance and the kernel trick. With weight annealing on AS-Distance and KL-Divergence, the AS-IntroVAE are able to generate stable and high-quality images. The posterior collapse problem is addressed by making per-batch attempts to transform the image so that it better fits the prior distribution in the latent space. Compared with the per-image approach, this strategy fosters more diverse distributions in the latent space, allowing our model to produce images of great diversity. Comprehensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of AS-IntroVAE on image generation and reconstruction tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge