Anticipatory Detection of Compulsive Body-focused Repetitive Behaviors with Wearables
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2021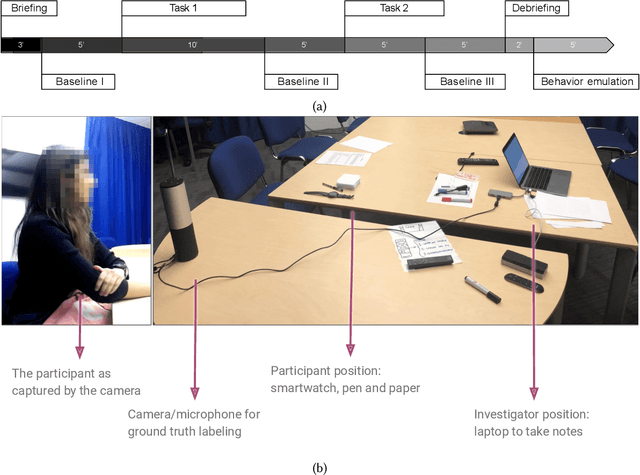
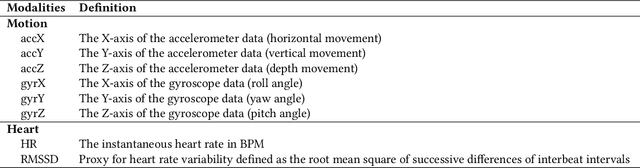
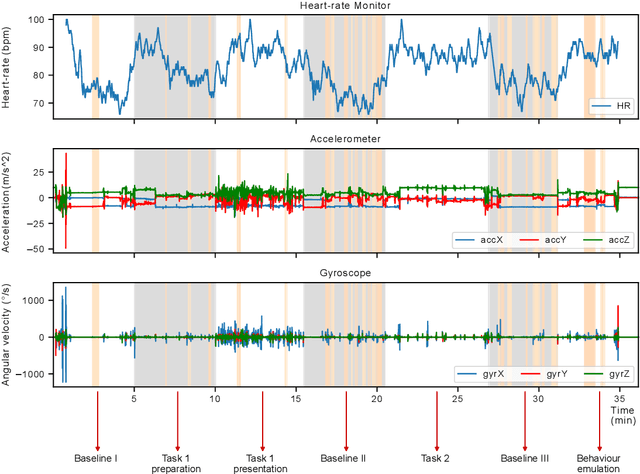
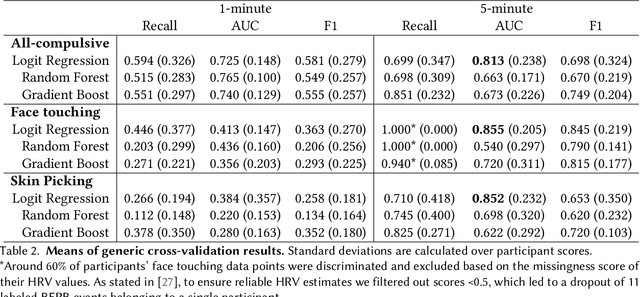
Body-focused repetitive behaviors (BFRBs), like face-touching or skin-picking, are hand-driven behaviors which can damage one's appearance, if not identified early and treated. Technology for automatic detection is still under-explored, with few previous works being limited to wearables with single modalities (e.g., motion). Here, we propose a multi-sensory approach combining motion, orientation, and heart rate sensors to detect BFRBs. We conducted a feasibility study in which participants (N=10) were exposed to BFRBs-inducing tasks, and analyzed 380 mins of signals under an extensive evaluation of sensing modalities, cross-validation methods, and observation windows. Our models achieved an AUC > 0.90 in distinguishing BFRBs, which were more evident in observation windows 5 mins prior to the behavior as opposed to 1-min ones. In a follow-up qualitative survey, we found that not only the timing of detection matters but also models need to be context-aware, when designing just-in-time interventions to prevent BFRBs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge