ANNA: Enhanced Language Representation for Question Answering
Paper and Code
Apr 04, 2022
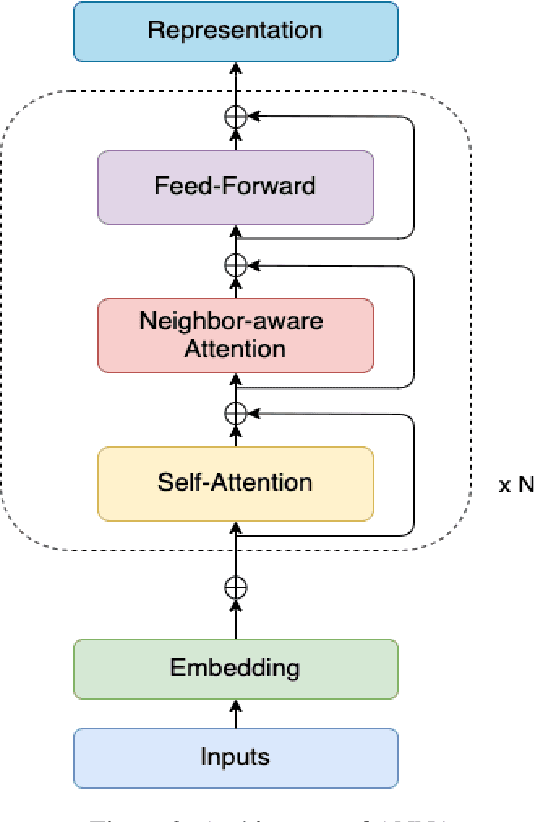
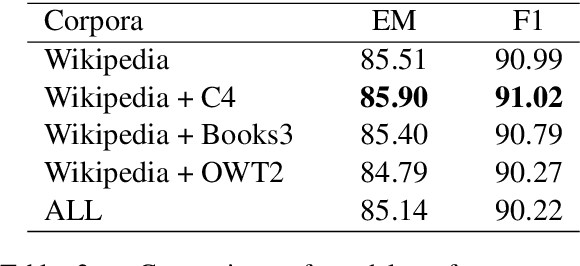
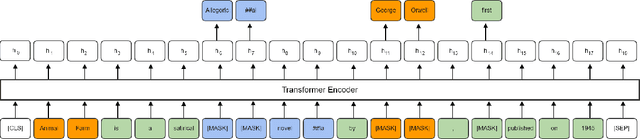
Pre-trained language models have brought significant improvements in performance in a variety of natural language processing tasks. Most existing models performing state-of-the-art results have shown their approaches in the separate perspectives of data processing, pre-training tasks, neural network modeling, or fine-tuning. In this paper, we demonstrate how the approaches affect performance individually, and that the language model performs the best results on a specific question answering task when those approaches are jointly considered in pre-training models. In particular, we propose an extended pre-training task, and a new neighbor-aware mechanism that attends neighboring tokens more to capture the richness of context for pre-training language modeling. Our best model achieves new state-of-the-art results of 95.7\% F1 and 90.6\% EM on SQuAD 1.1 and also outperforms existing pre-trained language models such as RoBERTa, ALBERT, ELECTRA, and XLNet on the SQuAD 2.0 benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge