An Investigation of Interpretability Techniques for Deep Learning in Predictive Process Analytics
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2020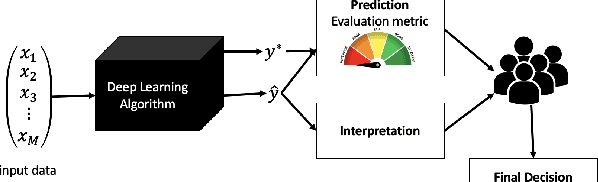
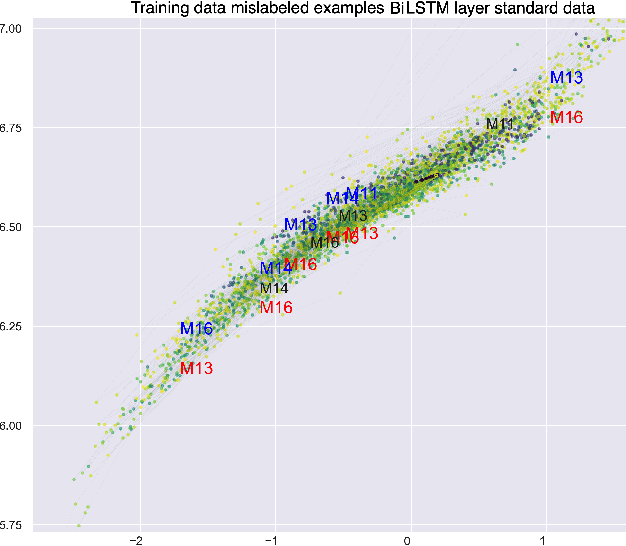
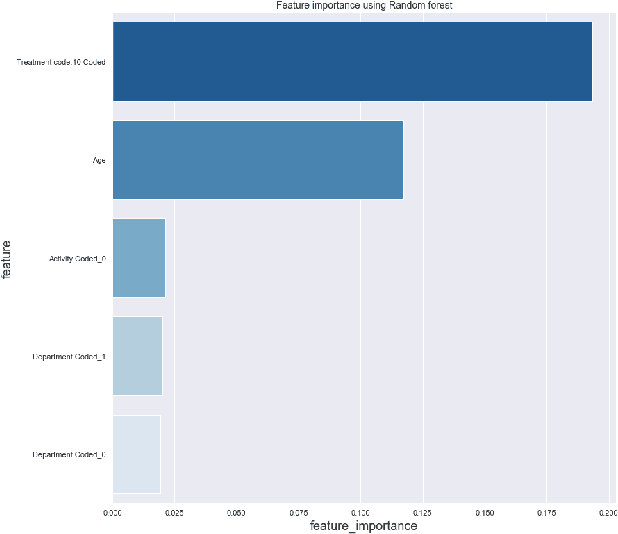

This paper explores interpretability techniques for two of the most successful learning algorithms in medical decision-making literature: deep neural networks and random forests. We applied these algorithms in a real-world medical dataset containing information about patients with cancer, where we learn models that try to predict the type of cancer of the patient, given their set of medical activity records. We explored different algorithms based on neural network architectures using long short term deep neural networks, and random forests. Since there is a growing need to provide decision-makers understandings about the logic of predictions of black boxes, we also explored different techniques that provide interpretations for these classifiers. In one of the techniques, we intercepted some hidden layers of these neural networks and used autoencoders in order to learn what is the representation of the input in the hidden layers. In another, we investigated an interpretable model locally around the random forest's prediction. Results show learning an interpretable model locally around the model's prediction leads to a higher understanding of why the algorithm is making some decision. Use of local and linear model helps identify the features used in prediction of a specific instance or data point. We see certain distinct features used for predictions that provide useful insights about the type of cancer, along with features that do not generalize well. In addition, the structured deep learning approach using autoencoders provided meaningful prediction insights, which resulted in the identification of nonlinear clusters correspondent to the patients' different types of cancer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge