An Effective Baseline for Robustness to Distributional Shift
Paper and Code
May 15, 2021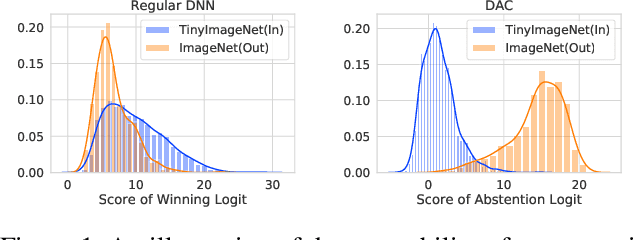
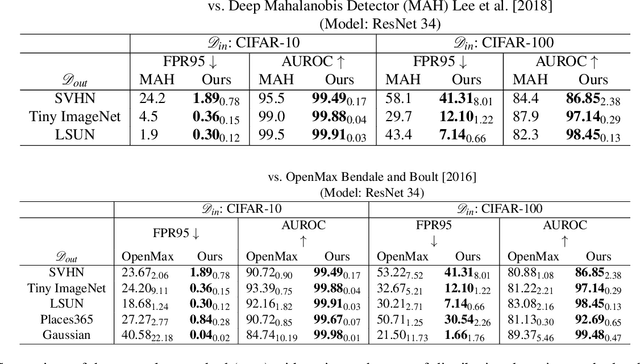
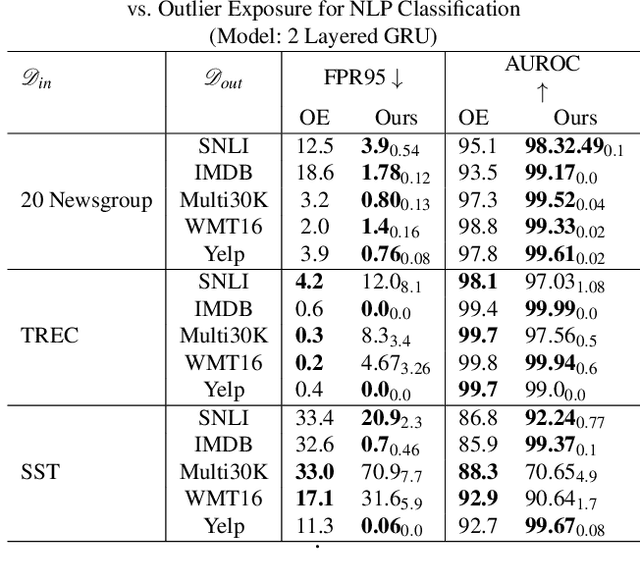
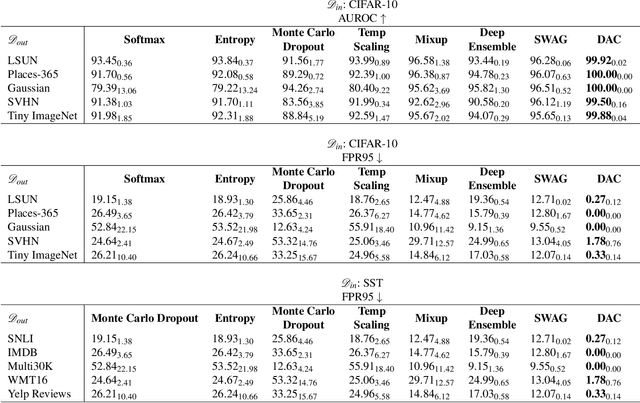
Refraining from confidently predicting when faced with categories of inputs different from those seen during training is an important requirement for the safe deployment of deep learning systems. While simple to state, this has been a particularly challenging problem in deep learning, where models often end up making overconfident predictions in such situations. In this work we present a simple, but highly effective approach to deal with out-of-distribution detection that uses the principle of abstention: when encountering a sample from an unseen class, the desired behavior is to abstain from predicting. Our approach uses a network with an extra abstention class and is trained on a dataset that is augmented with an uncurated set that consists of a large number of out-of-distribution (OoD) samples that are assigned the label of the abstention class; the model is then trained to learn an effective discriminator between in and out-of-distribution samples. We compare this relatively simple approach against a wide variety of more complex methods that have been proposed both for out-of-distribution detection as well as uncertainty modeling in deep learning, and empirically demonstrate its effectiveness on a wide variety of of benchmarks and deep architectures for image recognition and text classification, often outperforming existing approaches by significant margins. Given the simplicity and effectiveness of this method, we propose that this approach be used as a new additional baseline for future work in this domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge