An Adjustable Farthest Point Sampling Method for Approximately-sorted Point Cloud Data
Paper and Code
Aug 18, 2022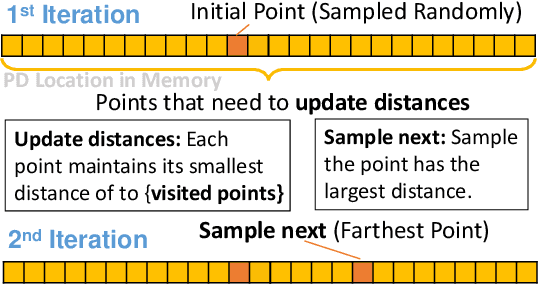
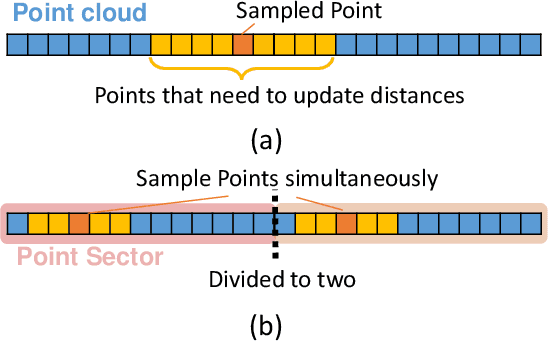
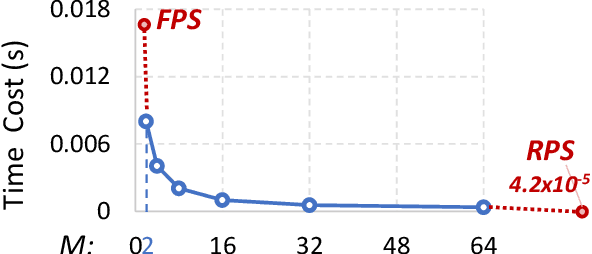
Sampling is an essential part of raw point cloud data processing such as in the popular PointNet++ scheme. Farthest Point Sampling (FPS), which iteratively samples the farthest point and performs distance updating, is one of the most popular sampling schemes. Unfortunately it suffers from low efficiency and can become the bottleneck of point cloud applications. We propose adjustable FPS (AFPS), parameterized by M, to aggressively reduce the complexity of FPS without compromising on the sampling performance. Specifically, it divides the original point cloud into M small point clouds and samples M points simultaneously. It exploits the dimensional locality of an approximately sorted point cloud data to minimize its performance degradation. AFPS method can achieve 22 to 30x speedup over original FPS. Furthermore, we propose the nearest-point-distance-updating (NPDU) method to limit the number of distance updates to a constant number. The combined NPDU on AFPS method can achieve a 34-280x speedup on a point cloud with 2K-32K points with algorithmic performance that is comparable to the original FPS. For instance, for the ShapeNet part segmentation task, it achieves 0.8490 instance average mIoU (mean Intersection of Union), which is only 0.0035 drop compared to the original FPS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge