Algorithmic Fairness and Vertical Equity: Income Fairness with IRS Tax Audit Models
Paper and Code
Jun 20, 2022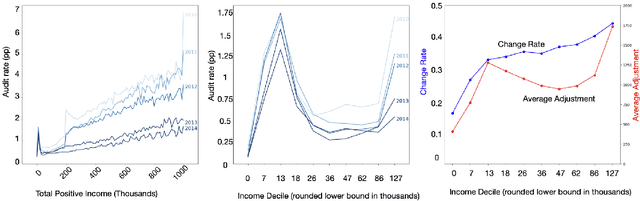
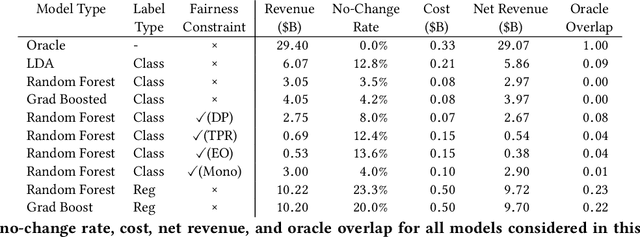
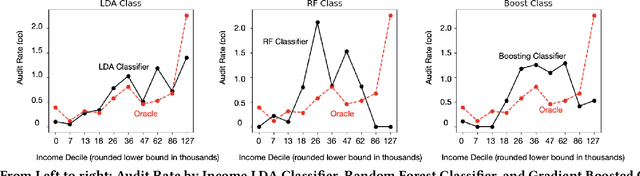
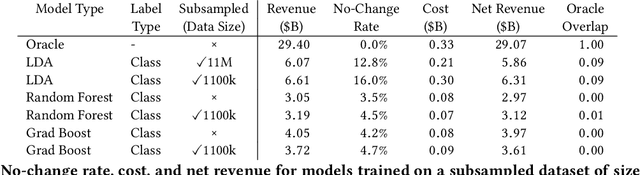
This study examines issues of algorithmic fairness in the context of systems that inform tax audit selection by the United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS). While the field of algorithmic fairness has developed primarily around notions of treating like individuals alike, we instead explore the concept of vertical equity -- appropriately accounting for relevant differences across individuals -- which is a central component of fairness in many public policy settings. Applied to the design of the U.S. individual income tax system, vertical equity relates to the fair allocation of tax and enforcement burdens across taxpayers of different income levels. Through a unique collaboration with the Treasury Department and IRS, we use access to anonymized individual taxpayer microdata, risk-selected audits, and random audits from 2010-14 to study vertical equity in tax administration. In particular, we assess how the use of modern machine learning methods for selecting audits may affect vertical equity. First, we show how the use of more flexible machine learning (classification) methods -- as opposed to simpler models -- shifts audit burdens from high to middle-income taxpayers. Second, we show that while existing algorithmic fairness techniques can mitigate some disparities across income, they can incur a steep cost to performance. Third, we show that the choice of whether to treat risk of underreporting as a classification or regression problem is highly consequential. Moving from classification to regression models to predict underreporting shifts audit burden substantially toward high income individuals, while increasing revenue. Last, we explore the role of differential audit cost in shaping the audit distribution. We show that a narrow focus on return-on-investment can undermine vertical equity. Our results have implications for the design of algorithmic tools across the public sector.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge