ADOD: Adaptive Domain-Aware Object Detection with Residual Attention for Underwater Environments
Paper and Code
Dec 11, 2023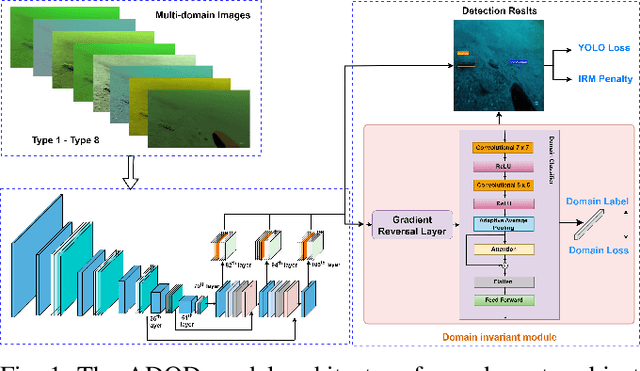
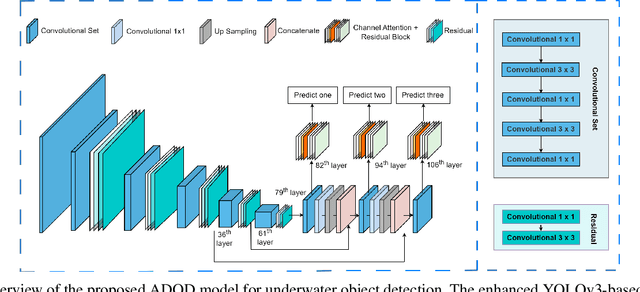
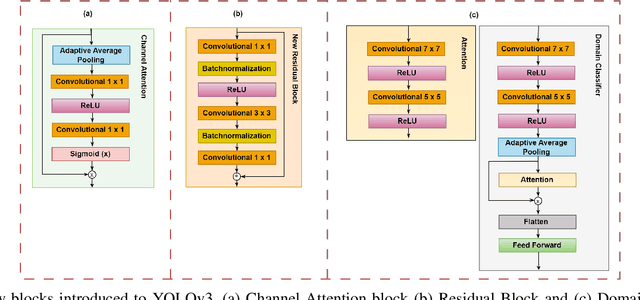
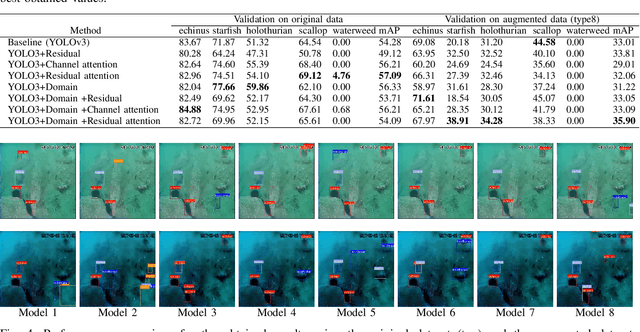
This research presents ADOD, a novel approach to address domain generalization in underwater object detection. Our method enhances the model's ability to generalize across diverse and unseen domains, ensuring robustness in various underwater environments. The first key contribution is Residual Attention YOLOv3, a novel variant of the YOLOv3 framework empowered by residual attention modules. These modules enable the model to focus on informative features while suppressing background noise, leading to improved detection accuracy and adaptability to different domains. The second contribution is the attention-based domain classification module, vital during training. This module helps the model identify domain-specific information, facilitating the learning of domain-invariant features. Consequently, ADOD can generalize effectively to underwater environments with distinct visual characteristics. Extensive experiments on diverse underwater datasets demonstrate ADOD's superior performance compared to state-of-the-art domain generalization methods, particularly in challenging scenarios. The proposed model achieves exceptional detection performance in both seen and unseen domains, showcasing its effectiveness in handling domain shifts in underwater object detection tasks. ADOD represents a significant advancement in adaptive object detection, providing a promising solution for real-world applications in underwater environments. With the prevalence of domain shifts in such settings, the model's strong generalization ability becomes a valuable asset for practical underwater surveillance and marine research endeavors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge