Accurate Calibration of Agent-based Epidemiological Models with Neural Network Surrogates
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2020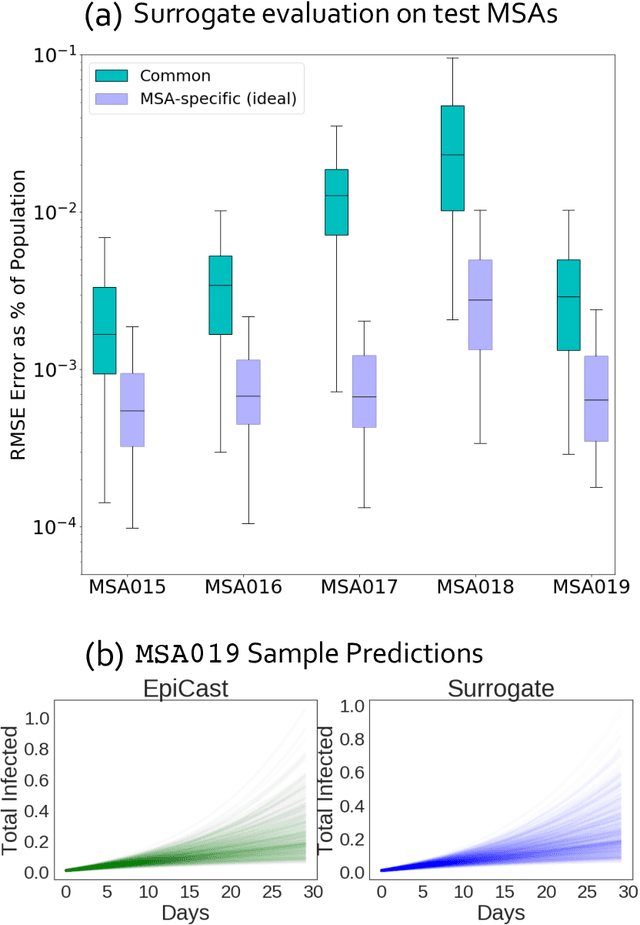
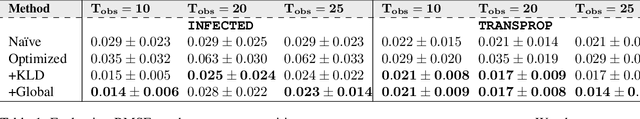
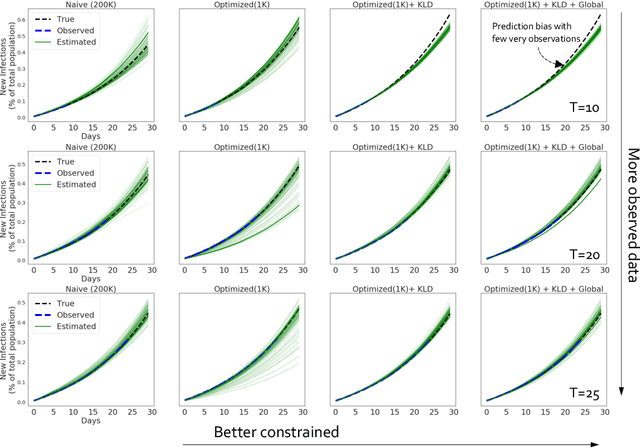
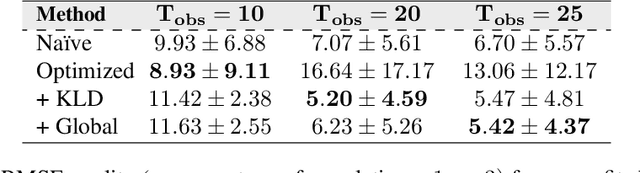
Calibrating complex epidemiological models to observed data is a crucial step to provide both insights into the current disease dynamics, i.e.\ by estimating a reproductive number, as well as to provide reliable forecasts and scenario explorations. Here we present a new approach to calibrate an agent-based model -- EpiCast -- using a large set of simulation ensembles for different major metropolitan areas of the United States. In particular, we propose: a new neural network based surrogate model able to simultaneously emulate all different locations; and a novel posterior estimation that provides not only more accurate posterior estimates of all parameters but enables the joint fitting of global parameters across regions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge