A Weak Monotonicity Based Muscle Fatigue Detection Algorithm for a Short-Duration Poor Posture Using sEMG Measurements
Paper and Code
Jun 18, 2021

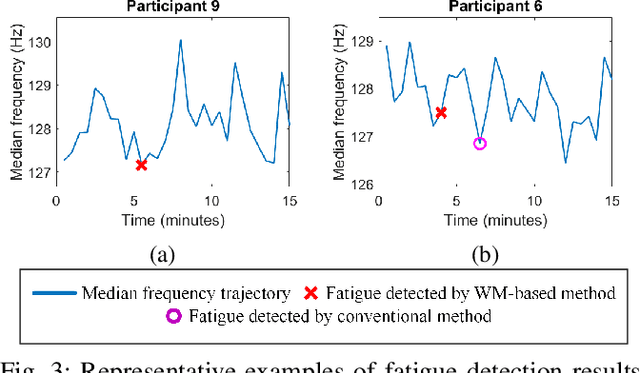
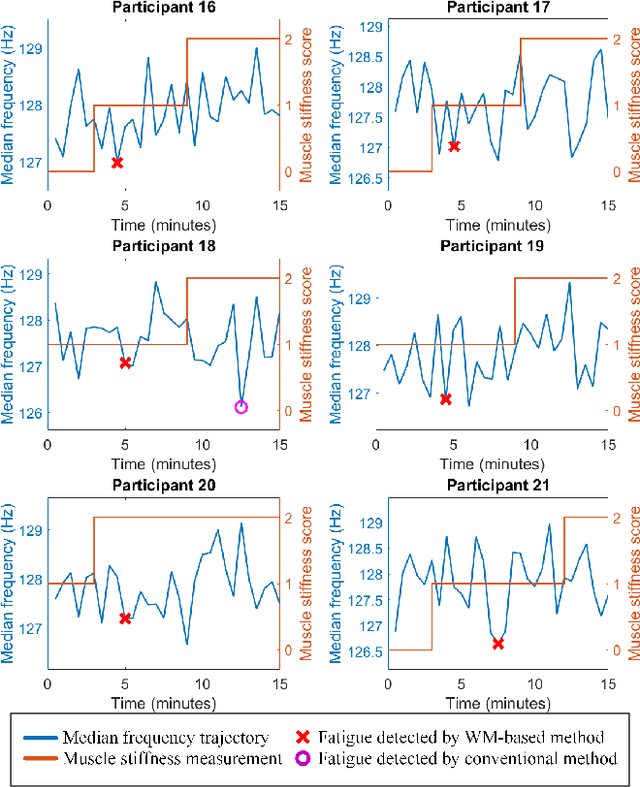
Muscle fatigue is usually defined as a decrease in the ability to produce force. The surface electromyography (sEMG) signals have been widely used to provide information about muscle activities including detecting muscle fatigue by various data-driven techniques such as machine learning and statistical approaches. However, it is well-known that sEMG signals are weak signals (low amplitude of the signals) with a low signal-to-noise ratio, data-driven techniques cannot work well when the quality of the data is poor. In particular, the existing methods are unable to detect muscle fatigue coming from static poses. This work exploits the concept of weak monotonicity, which has been observed in the process of fatigue, to robustly detect muscle fatigue in the presence of measurement noises and human variations. Such a population trend methodology has shown its potential in muscle fatigue detection as demonstrated by the experiment of a static pose.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge