A task-specific deep-learning-based denoising approach for myocardial perfusion SPECT
Paper and Code
Mar 01, 2023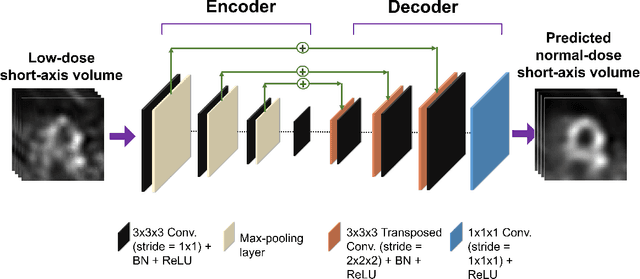
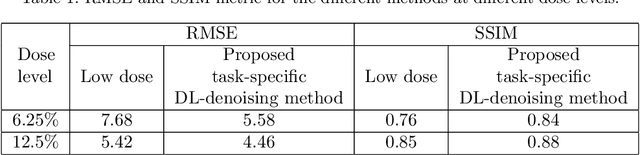
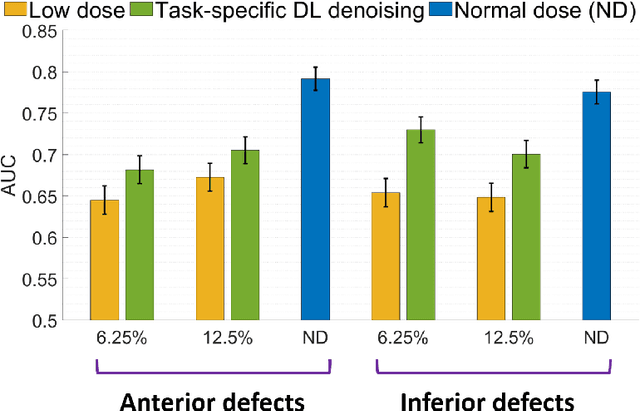
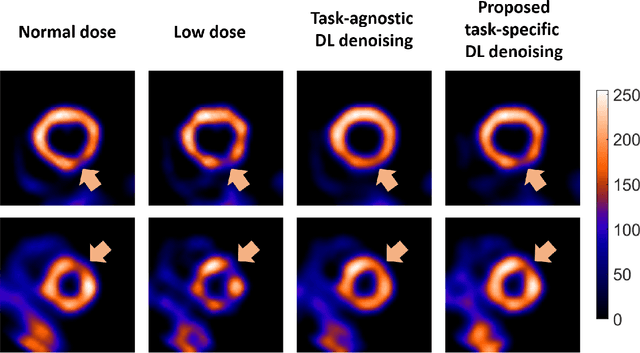
Deep-learning (DL)-based methods have shown significant promise in denoising myocardial perfusion SPECT images acquired at low dose. For clinical application of these methods, evaluation on clinical tasks is crucial. Typically, these methods are designed to minimize some fidelity-based criterion between the predicted denoised image and some reference normal-dose image. However, while promising, studies have shown that these methods may have limited impact on the performance of clinical tasks in SPECT. To address this issue, we use concepts from the literature on model observers and our understanding of the human visual system to propose a DL-based denoising approach designed to preserve observer-related information for detection tasks. The proposed method was objectively evaluated on the task of detecting perfusion defect in myocardial perfusion SPECT images using a retrospective study with anonymized clinical data. Our results demonstrate that the proposed method yields improved performance on this detection task compared to using low-dose images. The results show that by preserving task-specific information, DL may provide a mechanism to improve observer performance in low-dose myocardial perfusion SPECT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge