A switching Kalman filter approach to online mitigation and correction sensor corruption for inertial navigation
Paper and Code
Dec 09, 2024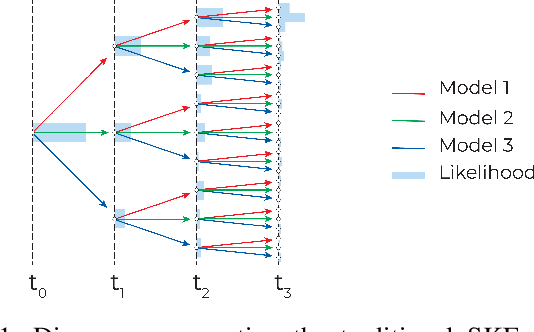
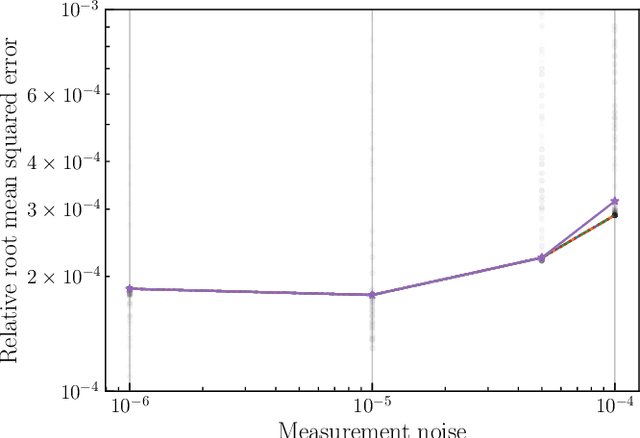
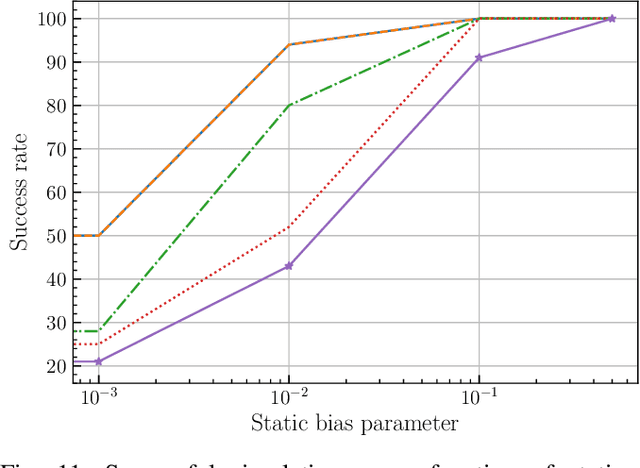
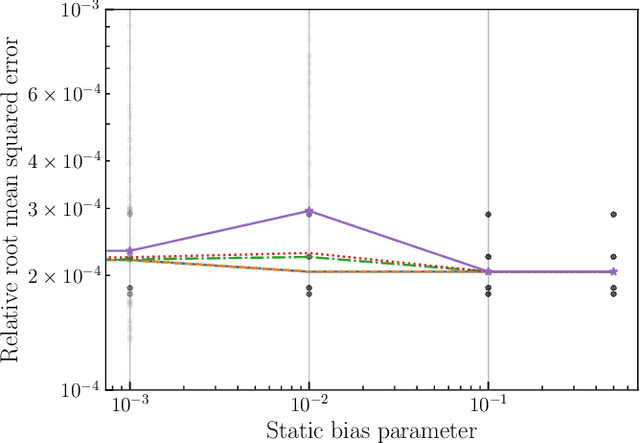
This paper introduces a novel approach to detect and address faulty or corrupted external sensors in the context of inertial navigation by leveraging a switching Kalman Filter combined with parameter augmentation. Instead of discarding the corrupted data, the proposed method retains and processes it, running multiple observation models simultaneously and evaluating their likelihoods to accurately identify the true state of the system. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach to both identify the moment that a sensor becomes faulty and to correct for the resulting sensor behavior to maintain accurate estimates. We demonstrate our approach on an application of balloon navigation in the atmosphere and shuttle reentry. The results show that our method can accurately recover the true system state even in the presence of significant sensor bias, thereby improving the robustness and reliability of state estimation systems under challenging conditions. We also provide a statistical analysis of problem settings to determine when and where our method is most accurate and where it fails.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge