A Study into Echocardiography View Conversion
Paper and Code
Dec 05, 2019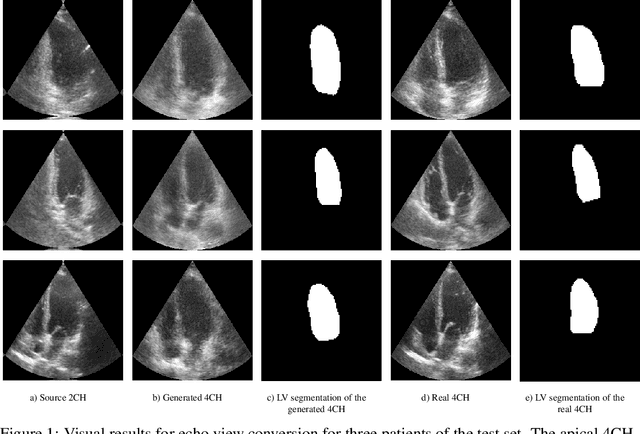
Transthoracic echo is one of the most common means of cardiac studies in the clinical routines. During the echo exam, the sonographer captures a set of standard cross sections (echo views) of the heart. Each 2D echo view cuts through the 3D cardiac geometry via a unique plane. Consequently, different views share some limited information. In this work, we investigate the feasibility of generating a 2D echo view using another view based on adversarial generative models. The objective optimized to train the view-conversion model is based on the ideas introduced by LSGAN, PatchGAN and Conditional GAN (cGAN). The size and length of the left ventricle in the generated target echo view is compared against that of the target ground-truth to assess the validity of the echo view conversion. Results show that there is a correlation of 0.50 between the LV areas and 0.49 between the LV lengths of the generated target frames and the real target frames.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge