A Static Analysis of Informed Down-Samples
Paper and Code
Apr 17, 2023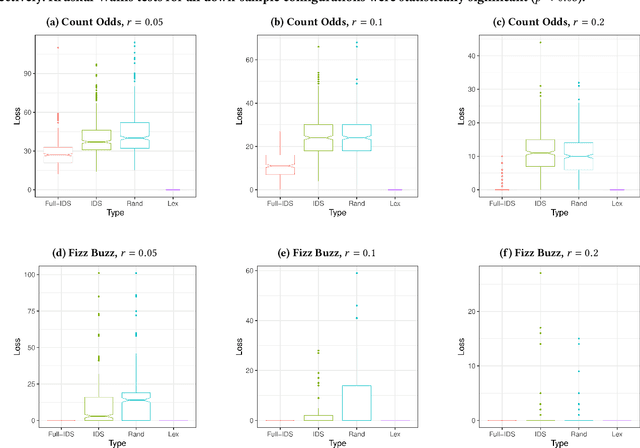
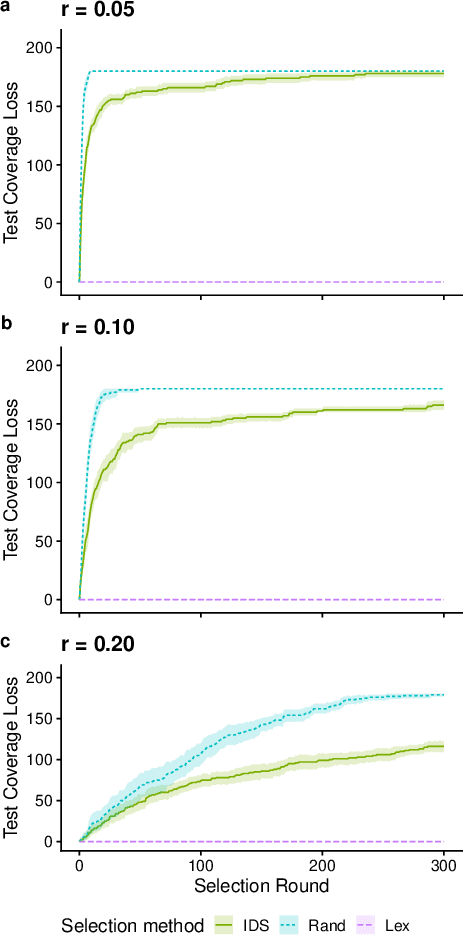
We present an analysis of the loss of population-level test coverage induced by different down-sampling strategies when combined with lexicase selection. We study recorded populations from the first generation of genetic programming runs, as well as entirely synthetic populations. Our findings verify the hypothesis that informed down-sampling better maintains population-level test coverage when compared to random down-sampling. Additionally, we show that both forms of down-sampling cause greater test coverage loss than standard lexicase selection with no down-sampling. However, given more information about the population, we found that informed down-sampling can further reduce its test coverage loss. We also recommend wider adoption of the static population analyses we present in this work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge