A Simple and Strong Baseline for Universal Targeted Attacks on Siamese Visual Tracking
Paper and Code
May 06, 2021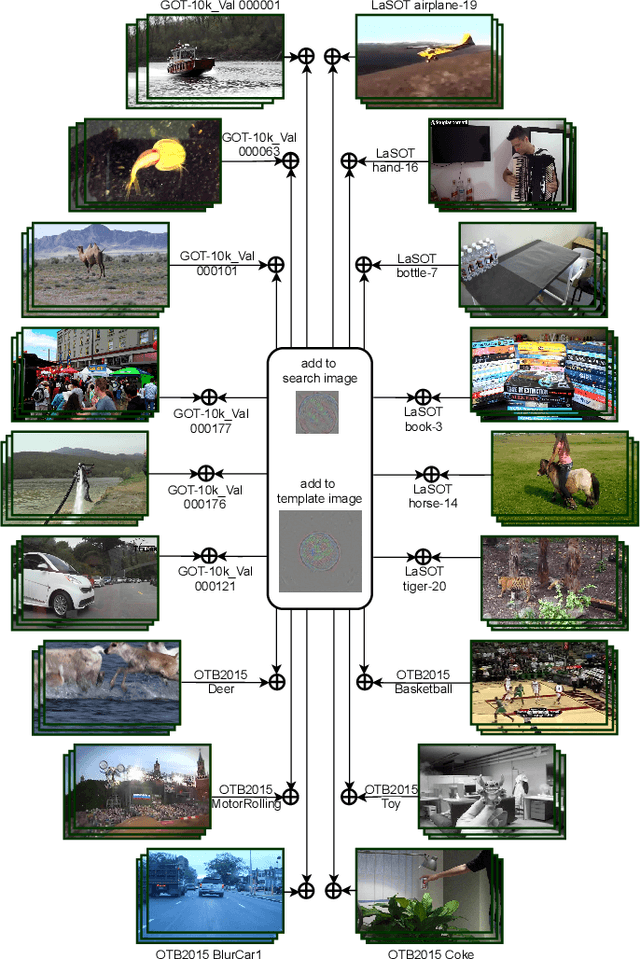
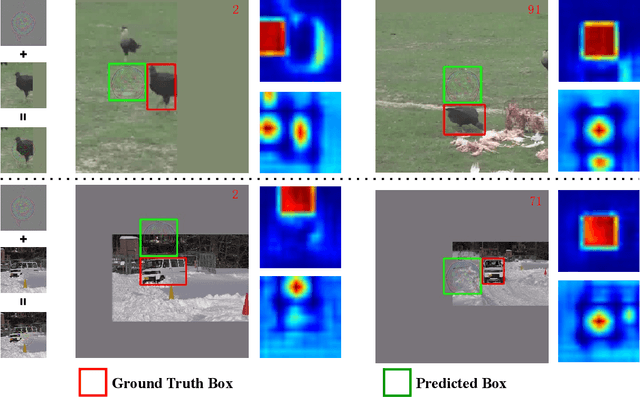
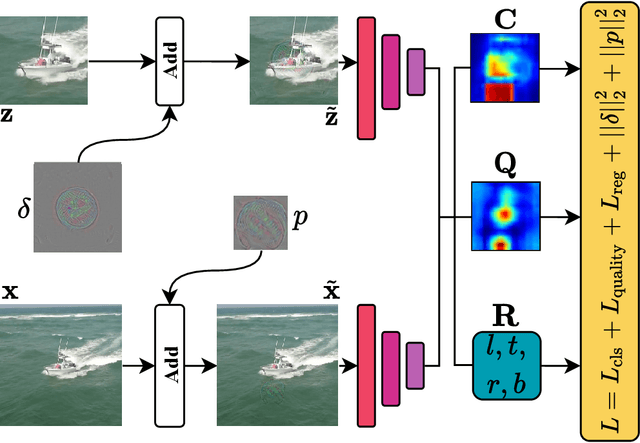

Siamese trackers are shown to be vulnerable to adversarial attacks recently. However, the existing attack methods craft the perturbations for each video independently, which comes at a non-negligible computational cost. In this paper, we show the existence of universal perturbations that can enable the targeted attack, e.g., forcing a tracker to follow the ground-truth trajectory with specified offsets, to be video-agnostic and free from inference in a network. Specifically, we attack a tracker by adding a universal imperceptible perturbation to the template image and adding a fake target, i.e., a small universal adversarial patch, into the search images adhering to the predefined trajectory, so that the tracker outputs the location and size of the fake target instead of the real target. Our approach allows perturbing a novel video to come at no additional cost except the mere addition operations -- and not require gradient optimization or network inference. Experimental results on several datasets demonstrate that our approach can effectively fool the Siamese trackers in a targeted attack manner. We show that the proposed perturbations are not only universal across videos, but also generalize well across different trackers. Such perturbations are therefore doubly universal, both with respect to the data and the network architectures. We will make our code publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge