A Physiologically-Adapted Gold Standard for Arousal during Stress
Paper and Code
Jul 28, 2021
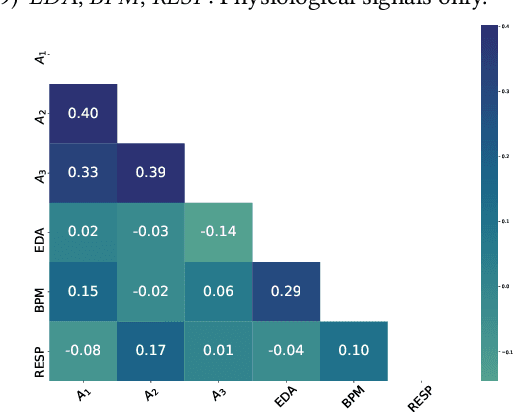
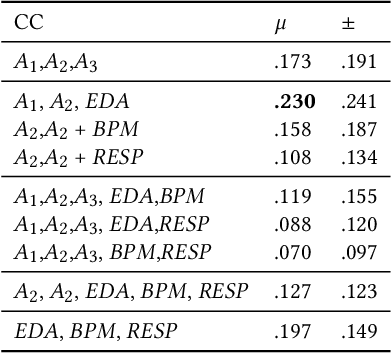
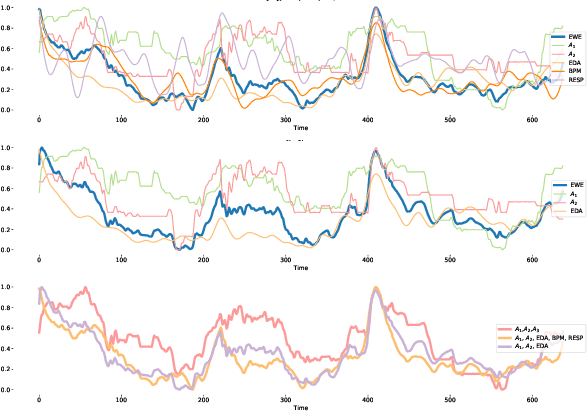
Emotion is an inherently subjective psychophysiological human-state and to produce an agreed-upon representation (gold standard) for continuous emotion requires a time-consuming and costly training procedure of multiple human annotators. There is strong evidence in the literature that physiological signals are sufficient objective markers for states of emotion, particularly arousal. In this contribution, we utilise a dataset which includes continuous emotion and physiological signals - Heartbeats per Minute (BPM), Electrodermal Activity (EDA), and Respiration-rate - captured during a stress inducing scenario (Trier Social Stress Test). We utilise a Long Short-Term Memory, Recurrent Neural Network to explore the benefit of fusing these physiological signals with arousal as the target, learning from various audio, video, and textual based features. We utilise the state-of-the-art MuSe-Toolbox to consider both annotation delay and inter-rater agreement weighting when fusing the target signals. An improvement in Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC) is seen across features sets when fusing EDA with arousal, compared to the arousal only gold standard results. Additionally, BERT-based textual features' results improved for arousal plus all physiological signals, obtaining up to .3344 CCC compared to .2118 CCC for arousal only. Multimodal fusion also improves overall CCC with audio plus video features obtaining up to .6157 CCC to recognize arousal plus EDA and BPM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge