A Novel Hybrid Endoscopic Dataset for Evaluating Machine Learning-based Photometric Image Enhancement Models
Paper and Code
Jul 06, 2022
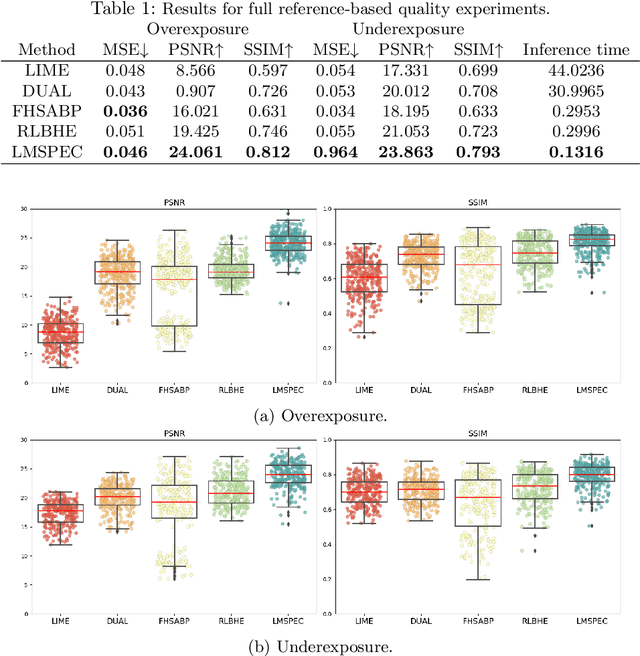
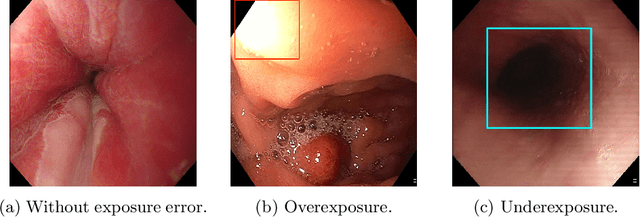
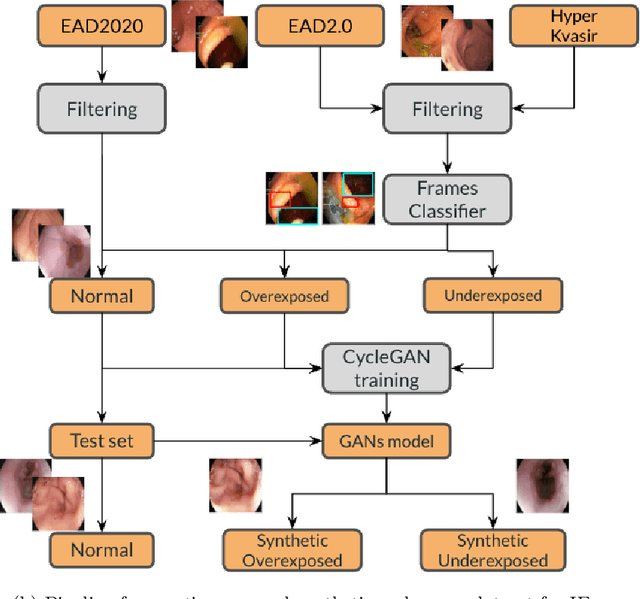
Endoscopy is the most widely used medical technique for cancer and polyp detection inside hollow organs. However, images acquired by an endoscope are frequently affected by illumination artefacts due to the enlightenment source orientation. There exist two major issues when the endoscope's light source pose suddenly changes: overexposed and underexposed tissue areas are produced. These two scenarios can result in misdiagnosis due to the lack of information in the affected zones or hamper the performance of various computer vision methods (e.g., SLAM, structure from motion, optical flow) used during the non invasive examination. The aim of this work is two-fold: i) to introduce a new synthetically generated data-set generated by a generative adversarial techniques and ii) and to explore both shallow based and deep learning-based image-enhancement methods in overexposed and underexposed lighting conditions. Best quantitative results (i.e., metric based results), were obtained by the deep-learnnig-based LMSPEC method,besides a running time around 7.6 fps)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge