A Novel Approach for Detection and Ranking of Trendy and Emerging Cyber Threat Events in Twitter Streams
Paper and Code
Jul 12, 2019

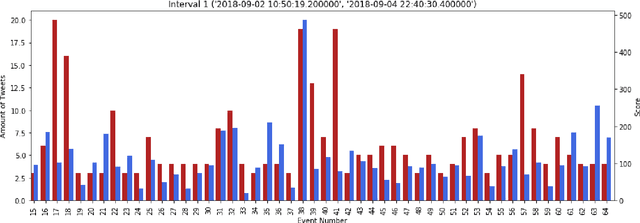
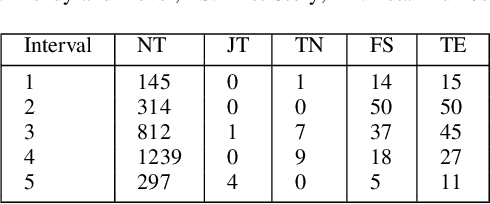
We present a new machine learning and text information extraction approach to detection of cyber threat events in Twitter that are novel (previously non-extant) and developing (marked by significance with respect to similarity with a previously detected event). While some existing approaches to event detection measure novelty and trendiness, typically as independent criteria and occasionally as a holistic measure, this work focuses on detecting both novel and developing events using an unsupervised machine learning approach. Furthermore, our proposed approach enables the ranking of cyber threat events based on an importance score by extracting the tweet terms that are characterized as named entities, keywords, or both. We also impute influence to users in order to assign a weighted score to noun phrases in proportion to user influence and the corresponding event scores for named entities and keywords. To evaluate the performance of our proposed approach, we measure the efficiency and detection error rate for events over a specified time interval, relative to human annotator ground truth.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge