A new perspective on classification: optimally allocating limited resources to uncertain tasks
Paper and Code
Feb 09, 2022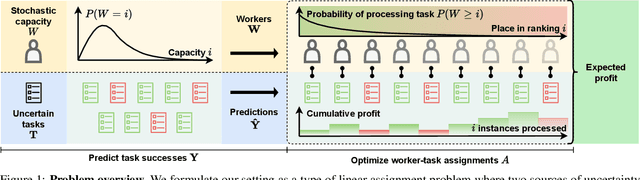
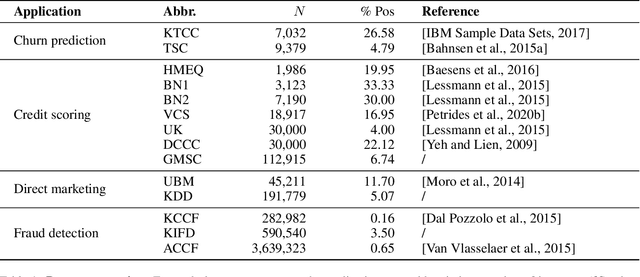
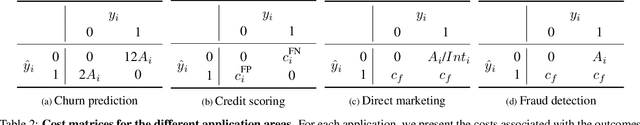
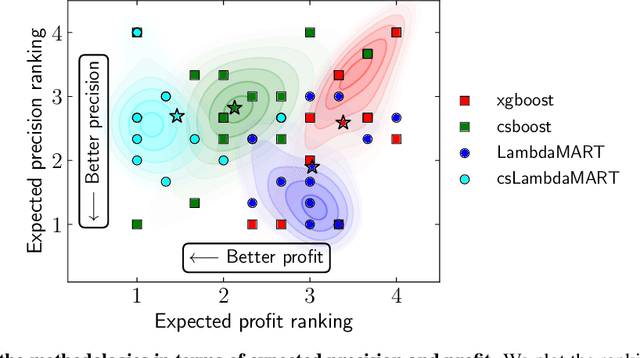
A central problem in business concerns the optimal allocation of limited resources to a set of available tasks, where the payoff of these tasks is inherently uncertain. In credit card fraud detection, for instance, a bank can only assign a small subset of transactions to their fraud investigations team. Typically, such problems are solved using a classification framework, where the focus is on predicting task outcomes given a set of characteristics. Resources are then allocated to the tasks that are predicted to be the most likely to succeed. However, we argue that using classification to address task uncertainty is inherently suboptimal as it does not take into account the available capacity. Therefore, we first frame the problem as a type of assignment problem. Then, we present a novel solution using learning to rank by directly optimizing the assignment's expected profit given limited, stochastic capacity. This is achieved by optimizing a specific instance of the net discounted cumulative gain, a commonly used class of metrics in learning to rank. Empirically, we demonstrate that our new method achieves higher expected profit and expected precision compared to a classification approach for a wide variety of application areas and data sets. This illustrates the benefit of an integrated approach and of explicitly considering the available resources when learning a predictive model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge