A Maximum Likelihood Approach to Extract Polylines from 2-D Laser Range Scans
Paper and Code
Oct 23, 2019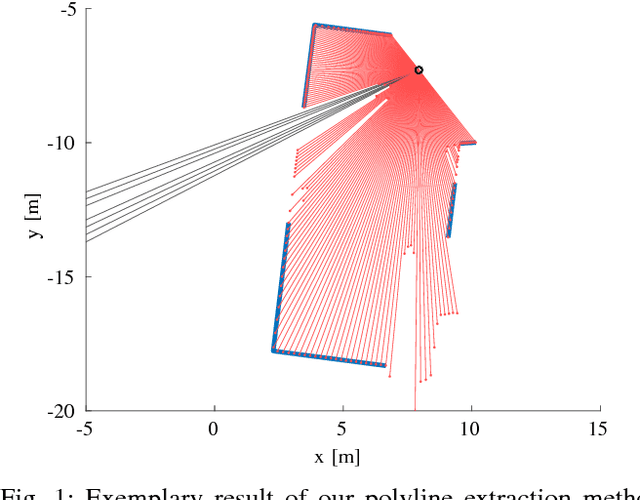
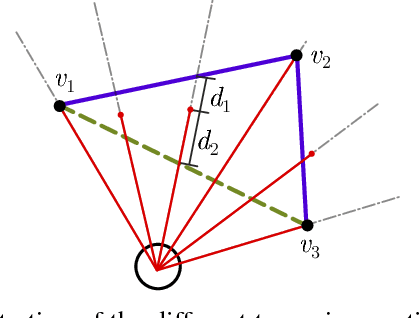
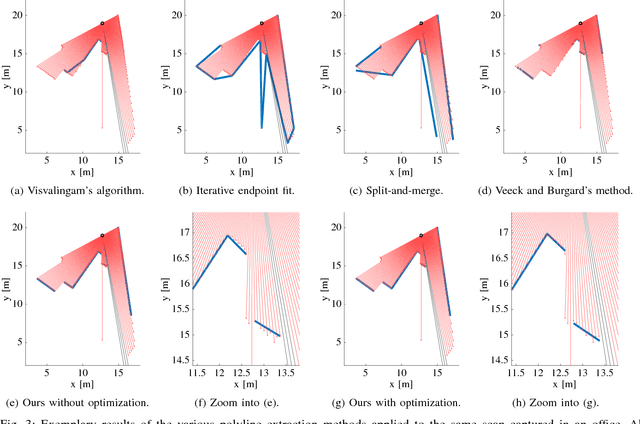
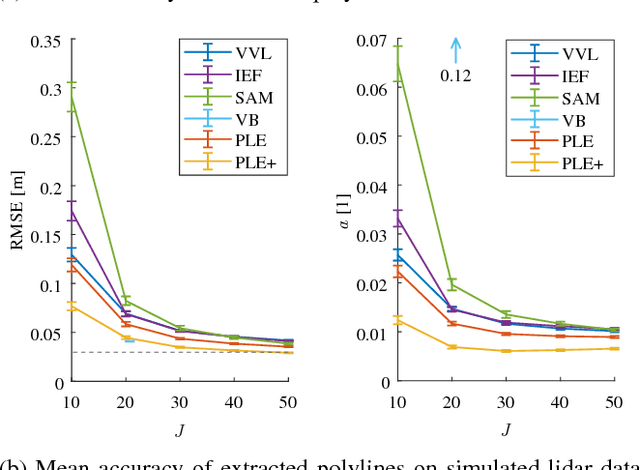
Man-made environments such as households, offices, or factory floors are typically composed of linear structures. Accordingly, polylines are a natural way to accurately represent their geometry. In this paper, we propose a novel probabilistic method to extract polylines from raw 2-D laser range scans. The key idea of our approach is to determine a set of polylines that maximizes the likelihood of a given scan. In extensive experiments carried out on publicly available real-world datasets and on simulated laser scans, we demonstrate that our method substantially outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches in terms of accuracy, while showing comparable computational requirements. Our implementation is available under https://github.com/acschaefer/ple.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge