A Lightweight Domain Adaptive Absolute Pose Regressor Using Barlow Twins Objective
Paper and Code
Nov 20, 2022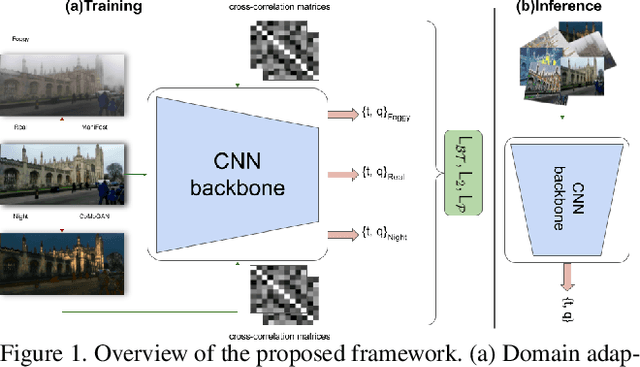
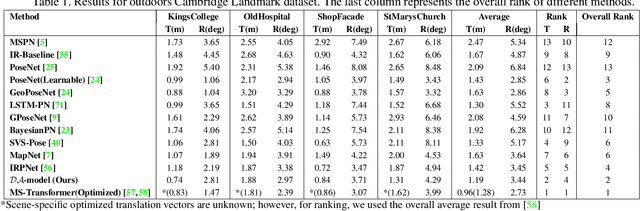
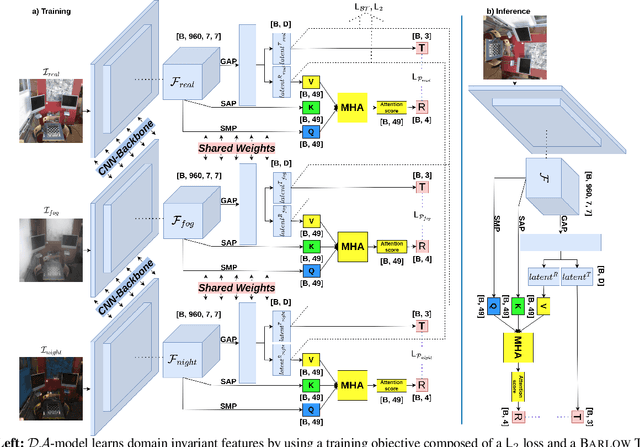
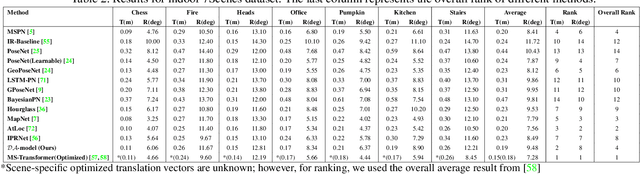
Identifying the camera pose for a given image is a challenging problem with applications in robotics, autonomous vehicles, and augmented/virtual reality. Lately, learning-based methods have shown to be effective for absolute camera pose estimation. However, these methods are not accurate when generalizing to different domains. In this paper, a domain adaptive training framework for absolute pose regression is introduced. In the proposed framework, the scene image is augmented for different domains by using generative methods to train parallel branches using Barlow Twins objective. The parallel branches leverage a lightweight CNN-based absolute pose regressor architecture. Further, the efficacy of incorporating spatial and channel-wise attention in the regression head for rotation prediction is investigated. Our method is evaluated with two datasets, Cambridge landmarks and 7Scenes. The results demonstrate that, even with using roughly 24 times fewer FLOPs, 12 times fewer activations, and 5 times fewer parameters than MS-Transformer, our approach outperforms all the CNN-based architectures and achieves performance comparable to transformer-based architectures. Our method ranks 2nd and 4th with the Cambridge Landmarks and 7Scenes datasets, respectively. In addition, for augmented domains not encountered during training, our approach significantly outperforms the MS-transformer. Furthermore, it is shown that our domain adaptive framework achieves better performance than the single branch model trained with the identical CNN backbone with all instances of the unseen distribution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge