A Guide Through the Zoo of Biased SGD
Paper and Code
May 25, 2023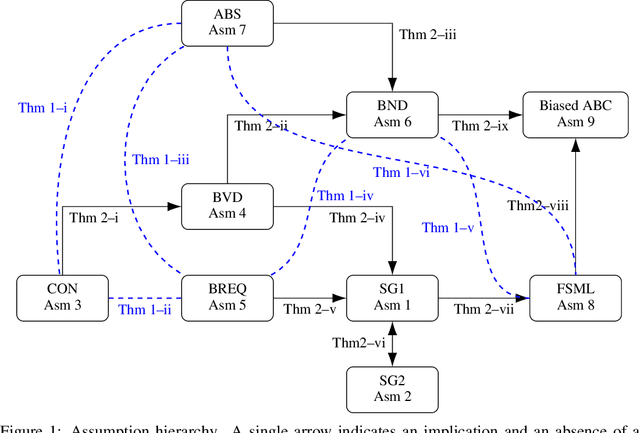

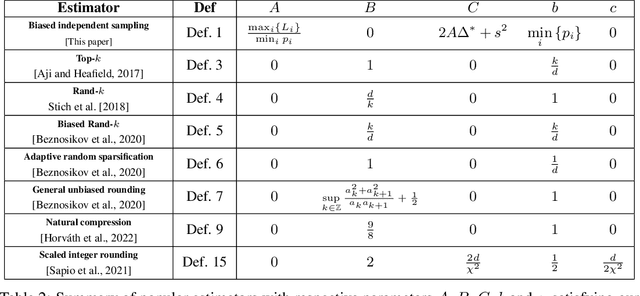
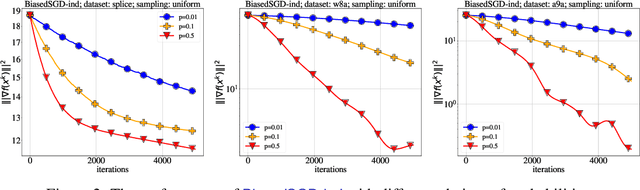
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) is arguably the most important single algorithm in modern machine learning. Although SGD with unbiased gradient estimators has been studied extensively over at least half a century, SGD variants relying on biased estimators are rare. Nevertheless, there has been an increased interest in this topic in recent years. However, existing literature on SGD with biased estimators (BiasedSGD) lacks coherence since each new paper relies on a different set of assumptions, without any clear understanding of how they are connected, which may lead to confusion. We address this gap by establishing connections among the existing assumptions, and presenting a comprehensive map of the underlying relationships. Additionally, we introduce a new set of assumptions that is provably weaker than all previous assumptions, and use it to present a thorough analysis of BiasedSGD in both convex and non-convex settings, offering advantages over previous results. We also provide examples where biased estimators outperform their unbiased counterparts or where unbiased versions are simply not available. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework through experimental results that validate our theoretical findings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge