A Deep Instance Generative Framework for MILP Solvers Under Limited Data Availability
Paper and Code
Oct 04, 2023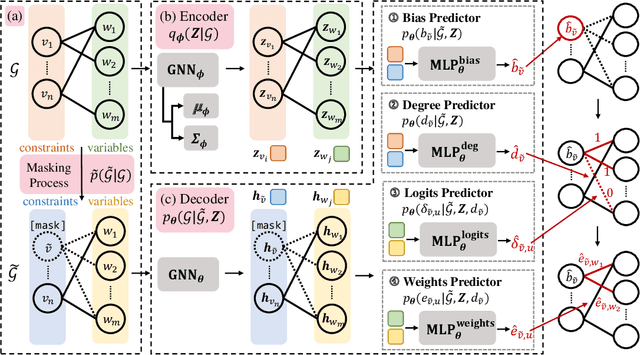
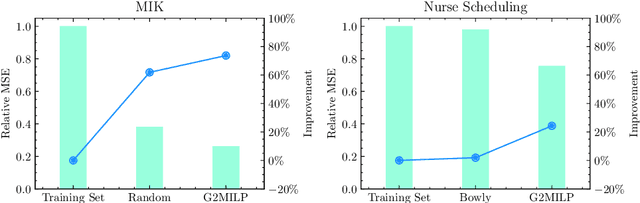
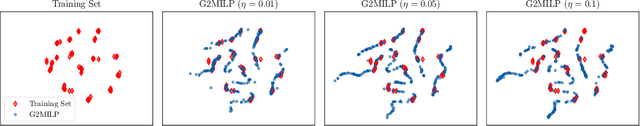
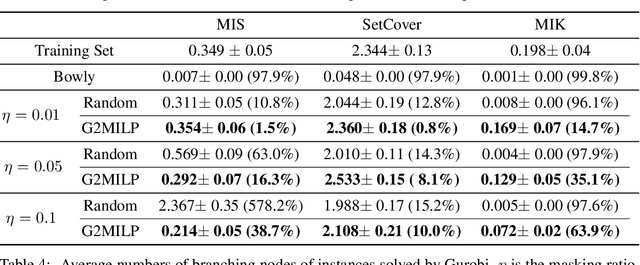
In the past few years, there has been an explosive surge in the use of machine learning (ML) techniques to address combinatorial optimization (CO) problems, especially mixed-integer linear programs (MILPs). Despite the achievements, the limited availability of real-world instances often leads to sub-optimal decisions and biased solver assessments, which motivates a suite of synthetic MILP instance generation techniques. However, existing methods either rely heavily on expert-designed formulations or struggle to capture the rich features of real-world instances. To tackle this problem, we propose G2MILP, which to the best of our knowledge is the first deep generative framework for MILP instances. Specifically, G2MILP represents MILP instances as bipartite graphs, and applies a masked variational autoencoder to iteratively corrupt and replace parts of the original graphs to generate new ones. The appealing feature of G2MILP is that it can learn to generate novel and realistic MILP instances without prior expert-designed formulations, while preserving the structures and computational hardness of real-world datasets, simultaneously. Thus the generated instances can facilitate downstream tasks for enhancing MILP solvers under limited data availability. We design a suite of benchmarks to evaluate the quality of the generated MILP instances. Experiments demonstrate that our method can produce instances that closely resemble real-world datasets in terms of both structures and computational hardness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge