A Debiased MDI Feature Importance Measure for Random Forests
Paper and Code
Jun 26, 2019
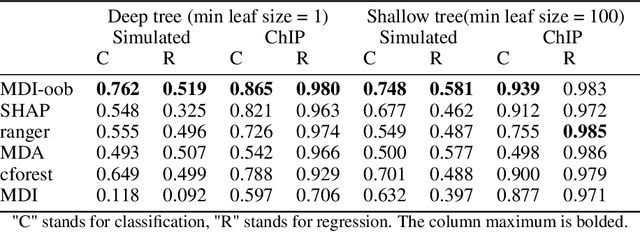
Tree ensembles such as Random Forests have achieved impressive empirical success across a wide variety of applications. To understand how these models make predictions, people routinely turn to feature importance measures calculated from tree ensembles. It has long been known that Mean Decrease Impurity (MDI), one of the most widely used measures of feature importance, incorrectly assigns high importance to noisy features, leading to systematic bias in feature selection. In this paper, we address the feature selection bias of MDI from both theoretical and methodological perspectives. Based on the original definition of MDI by Breiman et al. for a single tree, we derive a tight non-asymptotic bound on the expected bias of MDI importance of noisy features, showing that deep trees have higher (expected) feature selection bias than shallow ones. However, it is not clear how to reduce the bias of MDI using its existing analytical expression. We derive a new analytical expression for MDI, and based on this new expression, we are able to propose a debiased MDI feature importance measure using out-of-bag samples, called MDI-oob. For both the simulated data and a genomic ChIP dataset, MDI-oob achieves state-of-the-art performance in feature selection from Random Forests for both deep and shallow trees.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge