A Conformer-based Waveform-domain Neural Acoustic Echo Canceller Optimized for ASR Accuracy
Paper and Code
May 06, 2022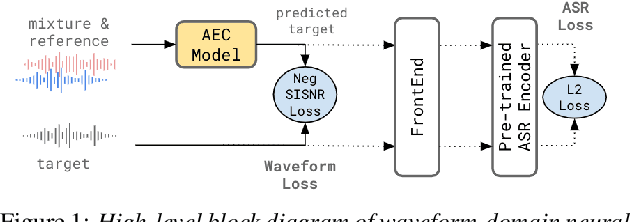
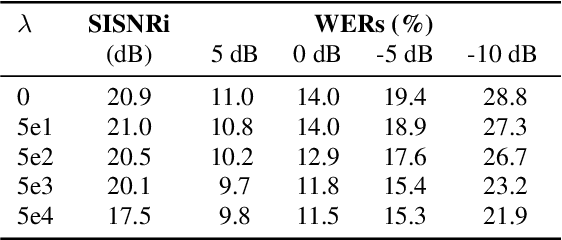
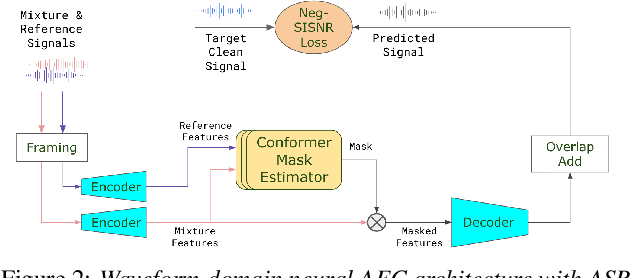
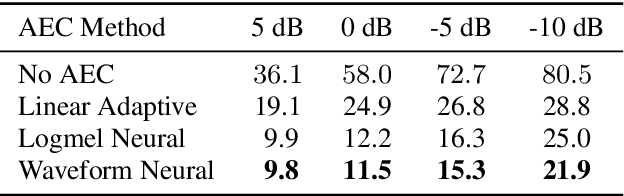
Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) is essential for accurate recognition of queries spoken to a smart speaker that is playing out audio. Previous work has shown that a neural AEC model operating on log-mel spectral features (denoted "logmel" hereafter) can greatly improve Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) accuracy when optimized with an auxiliary loss utilizing a pre-trained ASR model encoder. In this paper, we develop a conformer-based waveform-domain neural AEC model inspired by the "TasNet" architecture. The model is trained by jointly optimizing Negative Scale-Invariant SNR (SISNR) and ASR losses on a large speech dataset. On a realistic rerecorded test set, we find that cascading a linear adaptive AEC and a waveform-domain neural AEC is very effective, giving 56-59% word error rate (WER) reduction over the linear AEC alone. On this test set, the 1.6M parameter waveform-domain neural AEC also improves over a larger 6.5M parameter logmel-domain neural AEC model by 20-29% in easy to moderate conditions. By operating on smaller frames, the waveform neural model is able to perform better at smaller sizes and is better suited for applications where memory is limited.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge