A Chinese Spelling Check Framework Based on Reverse Contrastive Learning
Paper and Code
Oct 25, 2022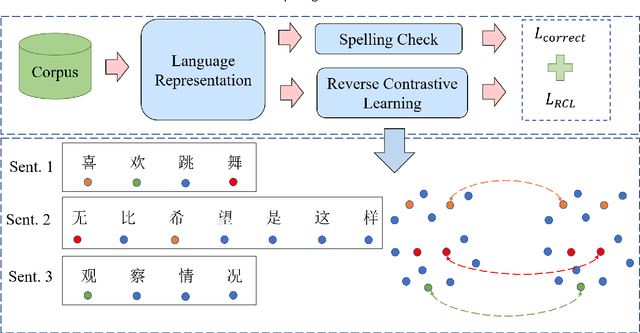
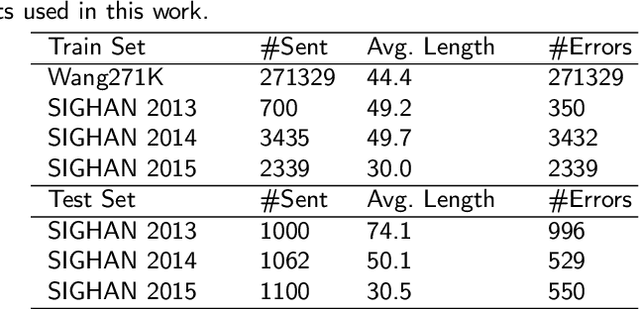
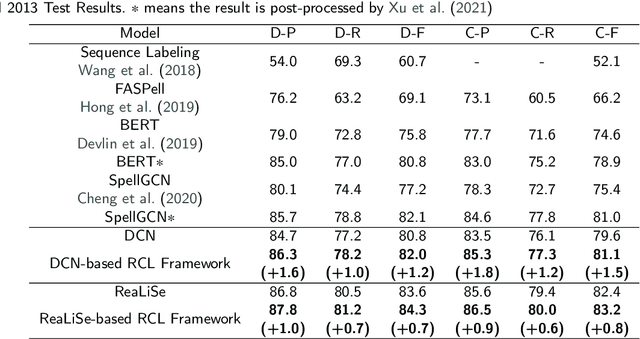
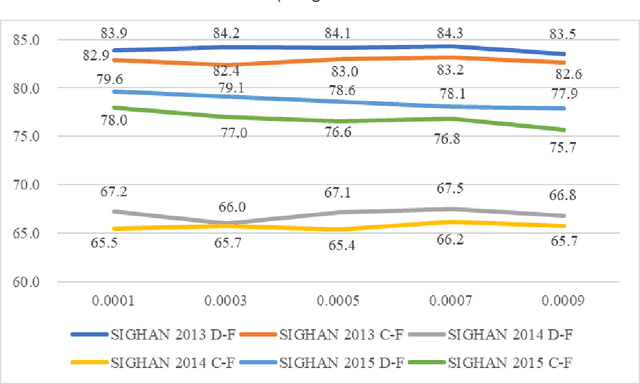
Chinese spelling check is a task to detect and correct spelling mistakes in Chinese text. Existing research aims to enhance the text representation and use multi-source information to improve the detection and correction capabilities of models, but does not pay too much attention to improving their ability to distinguish between confusable words. Contrastive learning, whose aim is to minimize the distance in representation space between similar sample pairs, has recently become a dominant technique in natural language processing. Inspired by contrastive learning, we present a novel framework for Chinese spelling checking, which consists of three modules: language representation, spelling check and reverse contrastive learning. Specifically, we propose a reverse contrastive learning strategy, which explicitly forces the model to minimize the agreement between the similar examples, namely, the phonetically and visually confusable characters. Experimental results show that our framework is model-agnostic and could be combined with existing Chinese spelling check models to yield state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge