Zuyuan Yang
FedMSGL: A Self-Expressive Hypergraph Based Federated Multi-View Learning
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Federated learning is essential for enabling collaborative model training across decentralized data sources while preserving data privacy and security. This approach mitigates the risks associated with centralized data collection and addresses concerns related to data ownership and compliance. Despite significant advancements in federated learning algorithms that address communication bottlenecks and enhance privacy protection, existing works overlook the impact of differences in data feature dimensions, resulting in global models that disproportionately depend on participants with large feature dimensions. Additionally, current single-view federated learning methods fail to account for the unique characteristics of multi-view data, leading to suboptimal performance in processing such data. To address these issues, we propose a Self-expressive Hypergraph Based Federated Multi-view Learning method (FedMSGL). The proposed method leverages self-expressive character in the local training to learn uniform dimension subspace with latent sample relation. At the central side, an adaptive fusion technique is employed to generate the global model, while constructing a hypergraph from the learned global and view-specific subspace to capture intricate interconnections across views. Experiments on multi-view datasets with different feature dimensions validated the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Partially Shared Semi-supervised Deep Matrix Factorization with Multi-view Data
Dec 02, 2020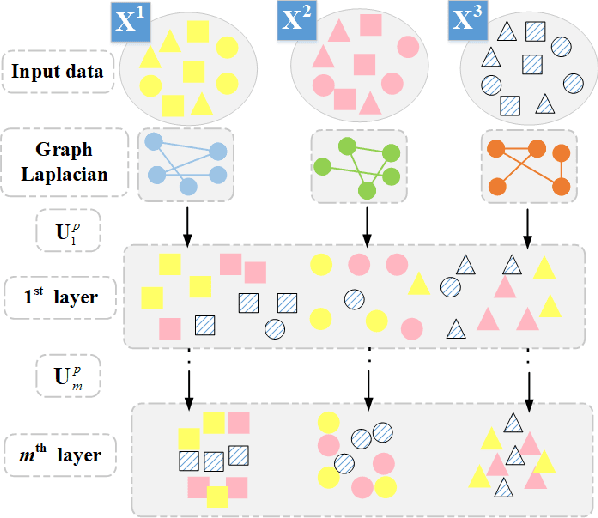
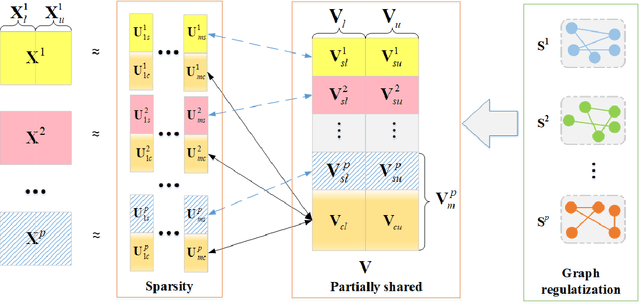
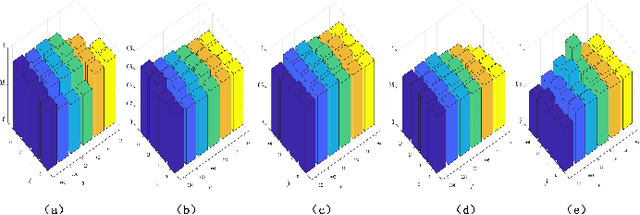
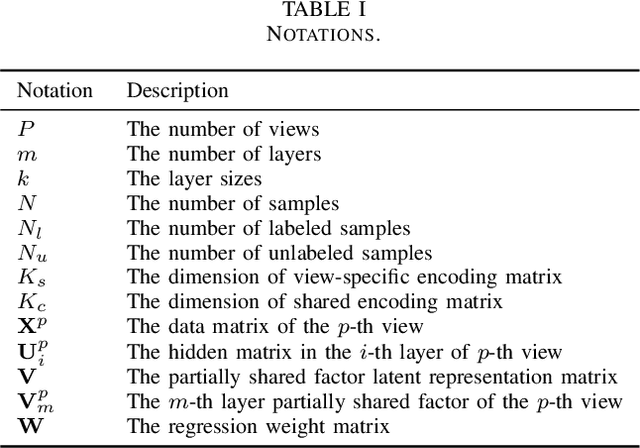
Abstract:Since many real-world data can be described from multiple views, multi-view learning has attracted considerable attention. Various methods have been proposed and successfully applied to multi-view learning, typically based on matrix factorization models. Recently, it is extended to the deep structure to exploit the hierarchical information of multi-view data, but the view-specific features and the label information are seldom considered. To address these concerns, we present a partially shared semi-supervised deep matrix factorization model (PSDMF). By integrating the partially shared deep decomposition structure, graph regularization and the semi-supervised regression model, PSDMF can learn a compact and discriminative representation through eliminating the effects of uncorrelated information. In addition, we develop an efficient iterative updating algorithm for PSDMF. Extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets demonstrate that PSDMF can achieve better performance than the state-of-the-art multi-view learning approaches. The MATLAB source code is available at https://github.com/libertyhhn/PartiallySharedDMF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge