Ziyi Ding
Step-by-Step Causality: Transparent Causal Discovery with Multi-Agent Tree-Query and Adversarial Confidence Estimation
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Causal discovery aims to recover ``what causes what'', but classical constraint-based methods (e.g., PC, FCI) suffer from error propagation, and recent LLM-based causal oracles often behave as opaque, confidence-free black boxes. This paper introduces Tree-Query, a tree-structured, multi-expert LLM framework that reduces pairwise causal discovery to a short sequence of queries about backdoor paths, (in)dependence, latent confounding, and causal direction, yielding interpretable judgments with robustness-aware confidence scores. Theoretical guarantees are provided for asymptotic identifiability of four pairwise relations. On data-free benchmarks derived from Mooij et al. and UCI causal graphs, Tree-Query improves structural metrics over direct LLM baselines, and a diet--weight case study illustrates confounder screening and stable, high-confidence causal conclusions. Tree-Query thus offers a principled way to obtain data-free causal priors from LLMs that can complement downstream data-driven causal discovery. Code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Repo-9B3E-4F96.
FIPGNet:Pyramid grafting network with feature interaction strategies
Jul 04, 2024
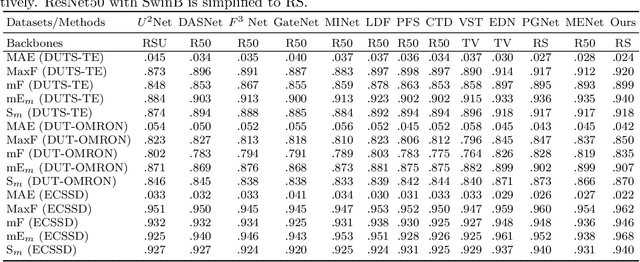
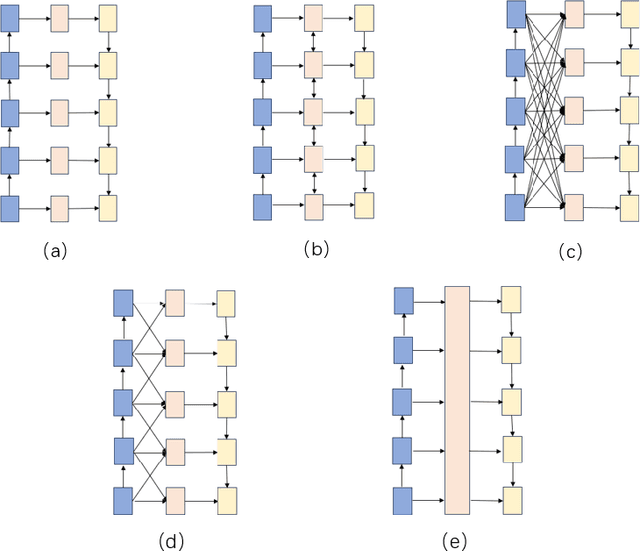
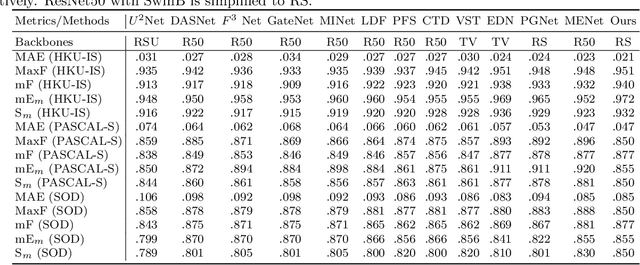
Abstract:Salient object detection is designed to identify the objects in an image that attract the most visual attention.Currently, the most advanced method of significance object detection adopts pyramid grafting network architecture.However, pyramid-graft network architecture still has the problem of failing to accurately locate significant targets.We observe that this is mainly due to the fact that current salient object detection methods simply aggregate different scale features, ignoring the correlation between different scale features.To overcome these problems, we propose a new salience object detection framework(FIPGNet),which is a pyramid graft network with feature interaction strategies.Specifically, we propose an attention-mechanism based feature interaction strategy (FIA) that innovatively introduces spatial agent Cross Attention (SACA) to achieve multi-level feature interaction, highlighting important spatial regions from a spatial perspective, thereby enhancing salient regions.And the channel proxy Cross Attention Module (CCM), which is used to effectively connect the features extracted by the backbone network and the features processed using the spatial proxy cross attention module, eliminating inconsistencies.Finally, under the action of these two modules, the prominent target location problem in the current pyramid grafting network model is solved.Experimental results on six challenging datasets show that the proposed method outperforms the current 12 salient object detection methods on four indicators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge