Zihuan Liu
A Role for Prior Knowledge in Statistical Classification of the Transition from MCI to Alzheimer's Disease
Nov 28, 2020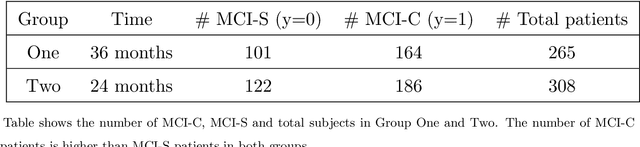
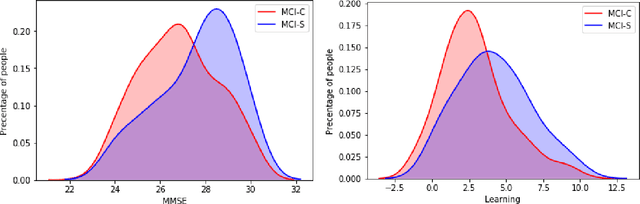
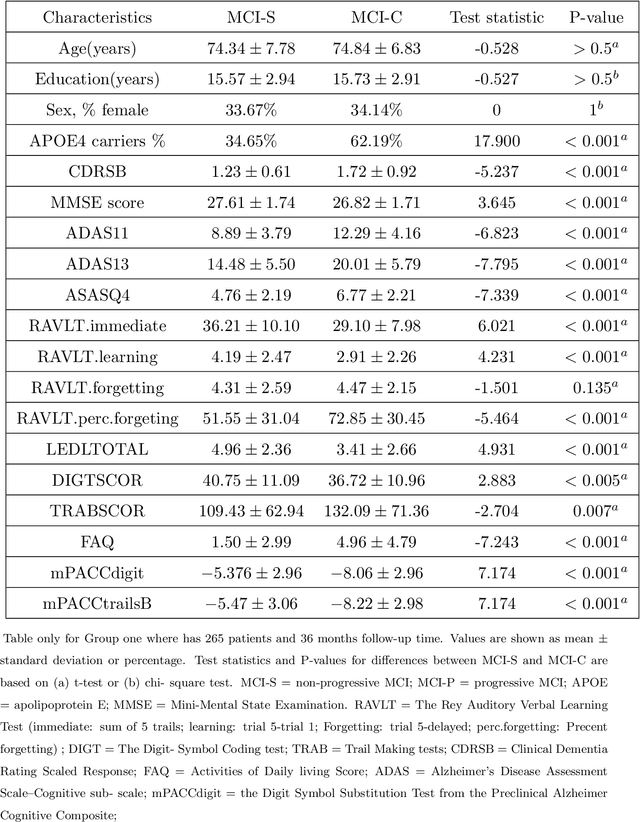
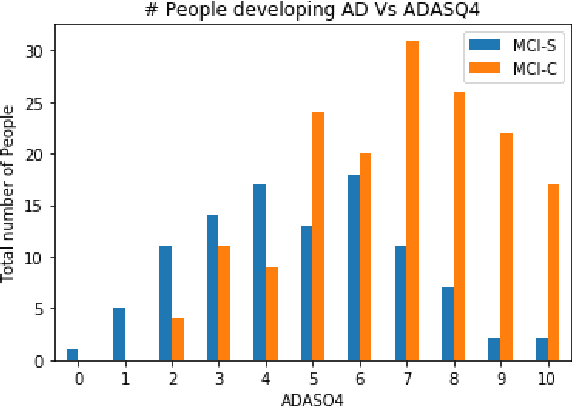
Abstract:The transition from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to Alzheimer's disease (AD) is of great interest to clinical researchers. This phenomenon also serves as a valuable data source for quantitative methodological researchers developing new approaches for classification. However, the growth of machine learning (ML) approaches for classification may falsely lead many clinical researchers to underestimate the value of logistic regression (LR), yielding equivalent or superior classification accuracy over other ML methods. Further, in applications with many features that could be used for classifying the transition, clinical researchers are often unaware of the relative value of different selection procedures. In the present study, we sought to investigate the use of automated and theoretically-guided feature selection techniques, and as well as the L-1 norm when applying different classification techniques for predicting conversion from MCI to AD in a highly characterized and studied sample from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI). We propose an alternative pre-selection technique that utilizes an efficient feature selection based on clinical knowledge of brain regions involved in AD. The present findings demonstrate how similar performance can be achieved using user-guided pre-selection versus algorithmic feature selection techniques. Finally, we compare the performance of a support vector machine (SVM) with that of logistic regression on multi-modal data from ADNI. The present findings show that although SVM and other ML techniques are capable of relatively accurate classification, similar or higher accuracy can often be achieved by LR, mitigating SVM's necessity or value for many clinical researchers.
Variational Bayes Neural Network: Posterior Consistency, Classification Accuracy and Computational Challenges
Nov 19, 2020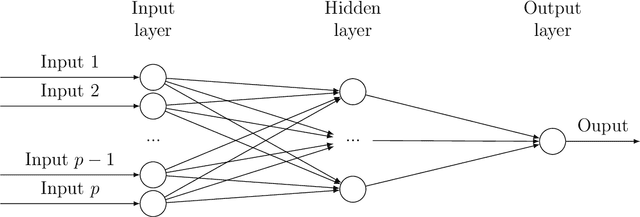
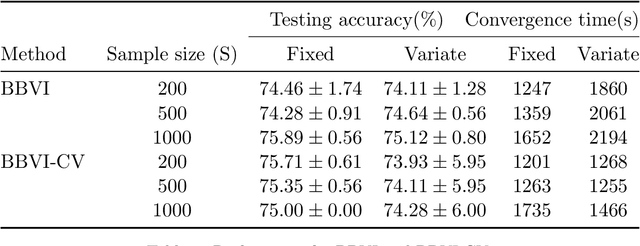
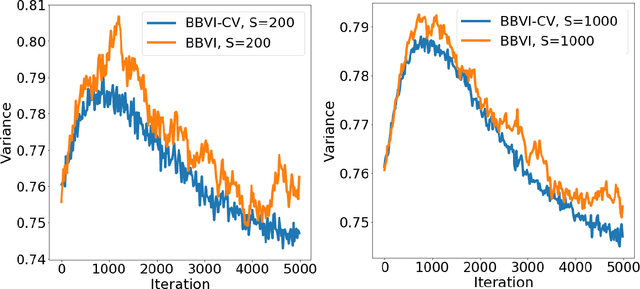

Abstract:Bayesian neural network models (BNN) have re-surged in recent years due to the advancement of scalable computations and its utility in solving complex prediction problems in a wide variety of applications. Despite the popularity and usefulness of BNN, the conventional Markov Chain Monte Carlo based implementation suffers from high computational cost, limiting the use of this powerful technique in large scale studies. The variational Bayes inference has become a viable alternative to circumvent some of the computational issues. Although the approach is popular in machine learning, its application in statistics is somewhat limited. This paper develops a variational Bayesian neural network estimation methodology and related statistical theory. The numerical algorithms and their implementational are discussed in detail. The theory for posterior consistency, a desirable property in nonparametric Bayesian statistics, is also developed. This theory provides an assessment of prediction accuracy and guidelines for characterizing the prior distributions and variational family. The loss of using a variational posterior over the true posterior has also been quantified. The development is motivated by an important biomedical engineering application, namely building predictive tools for the transition from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease. The predictors are multi-modal and may involve complex interactive relations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge