Zhenyuan Ning
DCMIL: A Progressive Representation Learning Model of Whole Slide Images for Cancer Prognosis Analysis
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:The burgeoning discipline of computational pathology shows promise in harnessing whole slide images (WSIs) to quantify morphological heterogeneity and develop objective prognostic modes for human cancers. However, progress is impeded by the computational bottleneck of gigapixel-size inputs and the scarcity of dense manual annotations. Current methods often overlook fine-grained information across multi-magnification WSIs and variations in tumor microenvironments. Here, we propose an easy-to-hard progressive representation learning model, termed dual-curriculum contrastive multi-instance learning (DCMIL), to efficiently process WSIs for cancer prognosis. The model does not rely on dense annotations and enables the direct transformation of gigapixel-size WSIs into outcome predictions. Extensive experiments on twelve cancer types (5,954 patients, 12.54 million tiles) demonstrate that DCMIL outperforms standard WSI-based prognostic models. Additionally, DCMIL identifies fine-grained prognosis-salient regions, provides robust instance uncertainty estimation, and captures morphological differences between normal and tumor tissues, with the potential to generate new biological insights. All codes have been made publicly accessible at https://github.com/tuuuc/DCMIL.
Decomposing and Coupling Saliency Map for Lesion Segmentation in Ultrasound Images
Aug 02, 2023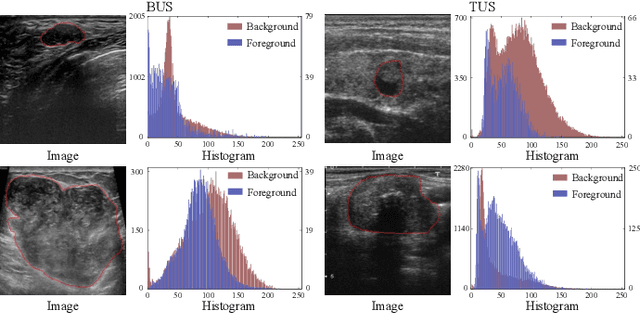

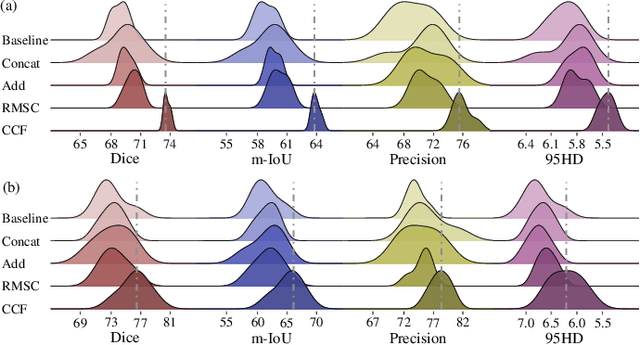
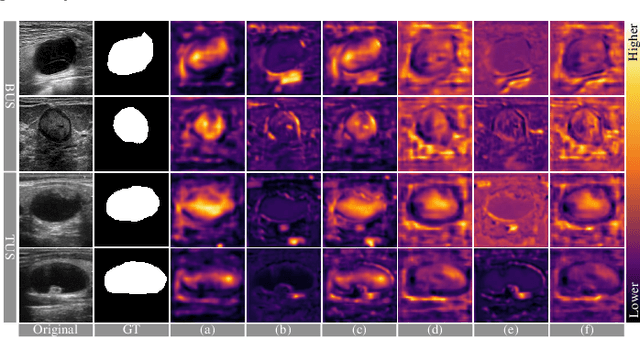
Abstract:Complex scenario of ultrasound image, in which adjacent tissues (i.e., background) share similar intensity with and even contain richer texture patterns than lesion region (i.e., foreground), brings a unique challenge for accurate lesion segmentation. This work presents a decomposition-coupling network, called DC-Net, to deal with this challenge in a (foreground-background) saliency map disentanglement-fusion manner. The DC-Net consists of decomposition and coupling subnets, and the former preliminarily disentangles original image into foreground and background saliency maps, followed by the latter for accurate segmentation under the assistance of saliency prior fusion. The coupling subnet involves three aspects of fusion strategies, including: 1) regional feature aggregation (via differentiable context pooling operator in the encoder) to adaptively preserve local contextual details with the larger receptive field during dimension reduction; 2) relation-aware representation fusion (via cross-correlation fusion module in the decoder) to efficiently fuse low-level visual characteristics and high-level semantic features during resolution restoration; 3) dependency-aware prior incorporation (via coupler) to reinforce foreground-salient representation with the complementary information derived from background representation. Furthermore, a harmonic loss function is introduced to encourage the network to focus more attention on low-confidence and hard samples. The proposed method is evaluated on two ultrasound lesion segmentation tasks, which demonstrates the remarkable performance improvement over existing state-of-the-art methods.
CF2-Net: Coarse-to-Fine Fusion Convolutional Network for Breast Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Mar 23, 2020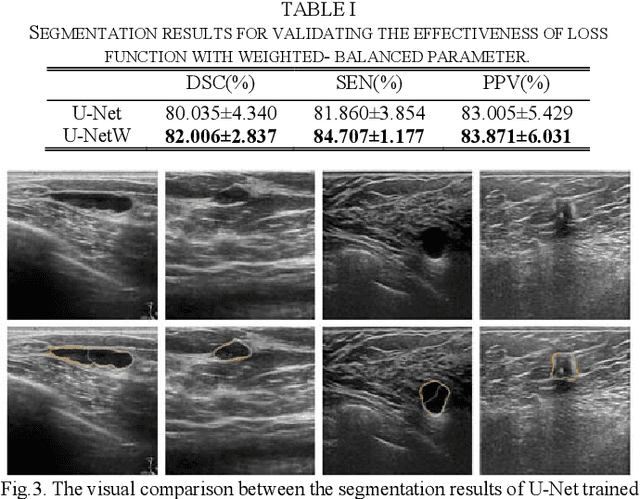
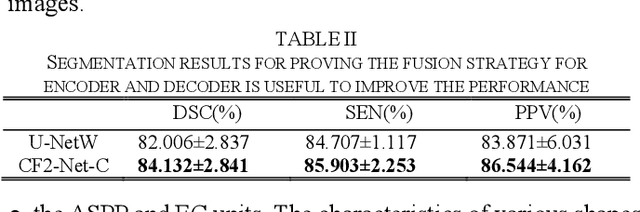
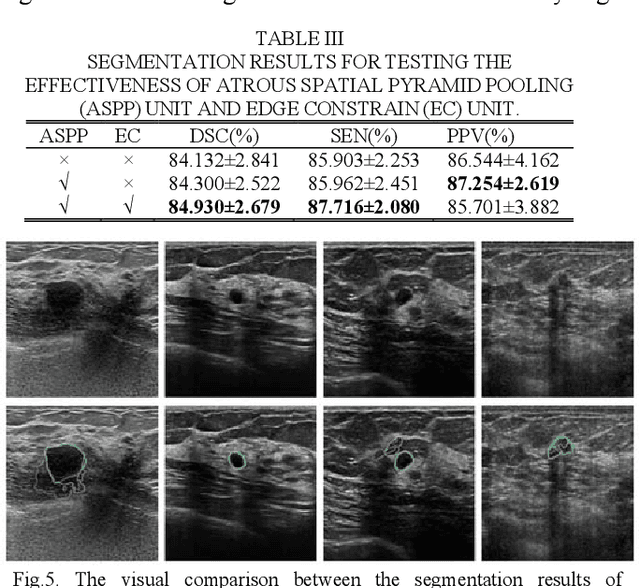
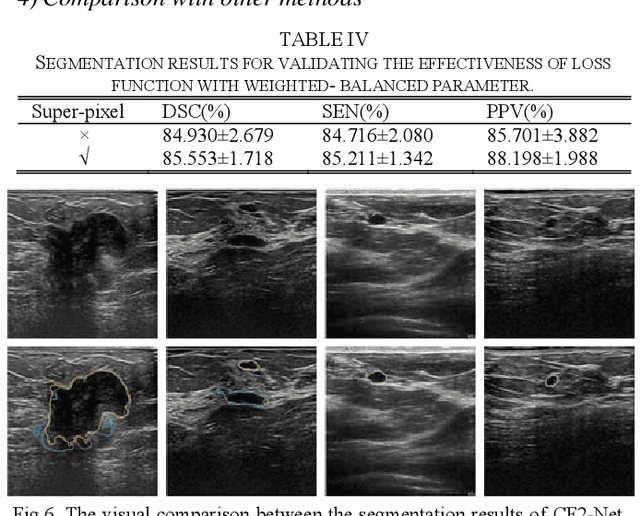
Abstract:Breast ultrasound (BUS) image segmentation plays a crucial role in a computer-aided diagnosis system, which is regarded as a useful tool to help increase the accuracy of breast cancer diagnosis. Recently, many deep learning methods have been developed for segmentation of BUS image and show some advantages compared with conventional region-, model-, and traditional learning-based methods. However, previous deep learning methods typically use skip-connection to concatenate the encoder and decoder, which might not make full fusion of coarse-to-fine features from encoder and decoder. Since the structure and edge of lesion in BUS image are common blurred, these would make it difficult to learn the discriminant information of structure and edge, and reduce the performance. To this end, we propose and evaluate a coarse-to-fine fusion convolutional network (CF2-Net) based on a novel feature integration strategy (forming an 'E'-like type) for BUS image segmentation. To enhance contour and provide structural information, we concatenate a super-pixel image and the original image as the input of CF2-Net. Meanwhile, to highlight the differences in the lesion regions with variable sizes and relieve the imbalance issue, we further design a weighted-balanced loss function to train the CF2-Net effectively. The proposed CF2-Net was evaluated on an open dataset by using four-fold cross validation. The results of the experiment demonstrate that the CF2-Net obtains state-of-the-art performance when compared with other deep learning-based methods
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge