Zhengwen Shen
EaDeblur-GS: Event assisted 3D Deblur Reconstruction with Gaussian Splatting
Jul 18, 2024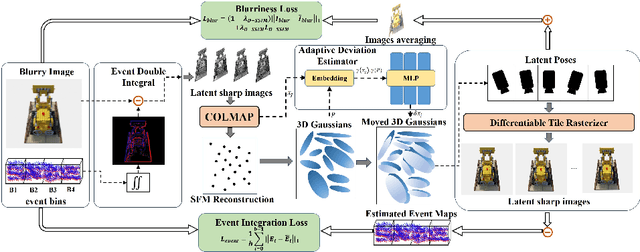

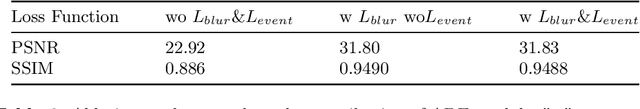
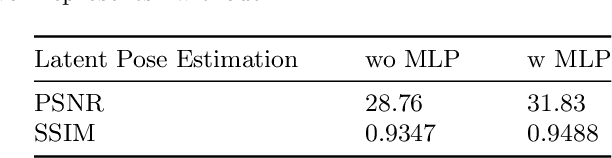
Abstract:3D deblurring reconstruction techniques have recently seen significant advancements with the development of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Although these techniques can recover relatively clear 3D reconstructions from blurry image inputs, they still face limitations in handling severe blurring and complex camera motion. To address these issues, we propose Event-assisted 3D Deblur Reconstruction with Gaussian Splatting (EaDeblur-GS), which integrates event camera data to enhance the robustness of 3DGS against motion blur. By employing an Adaptive Deviation Estimator (ADE) network to estimate Gaussian center deviations and using novel loss functions, EaDeblur-GS achieves sharp 3D reconstructions in real-time, demonstrating performance comparable to state-of-the-art methods.
Cross Attention-guided Dense Network for Images Fusion
Sep 23, 2021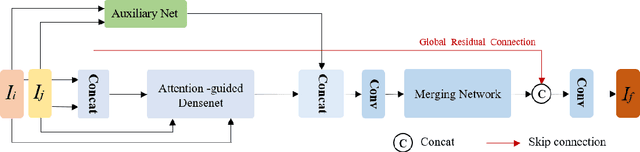
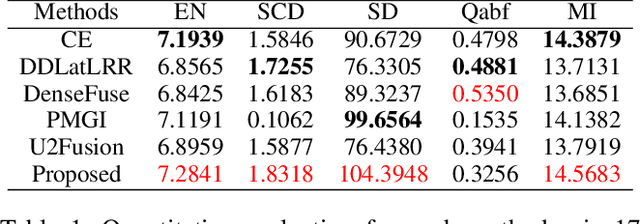
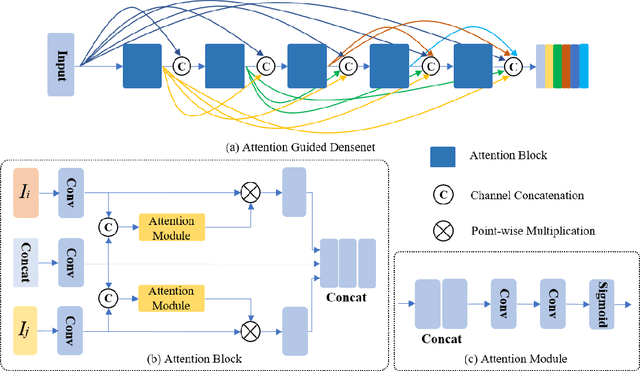
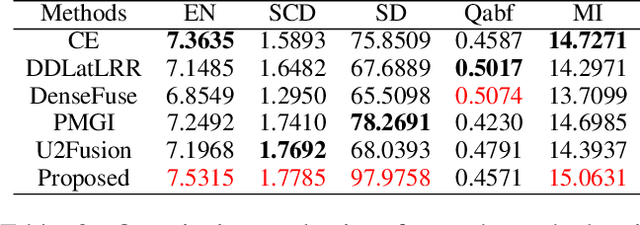
Abstract:In recent years, various applications in computer vision have achieved substantial progress based on deep learning, which has been widely used for image fusion and shown to achieve adequate performance. However, suffering from limited ability in modelling the spatial correspondence of different source images, it still remains a great challenge for existing unsupervised image fusion models to extract appropriate feature and achieves adaptive and balanced fusion. In this paper, we propose a novel cross attention-guided image fusion network, which is a unified and unsupervised framework for multi-modal image fusion, multi-exposure image fusion, and multi-focus image fusion. Different from the existing self-attention module, our cross attention module focus on modelling the cross-correlation between different source images. Using the proposed cross attention module as core block, a densely connected cross attention-guided network is built to dynamically learn the spatial correspondence to derive better alignment of important details from different input images. Meanwhile, an auxiliary branch is also designed to model the long-range information, and a merging network is attached to finally reconstruct the fusion image. Extensive experiments have been carried out on publicly available datasets, and the results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art quantitatively and qualitatively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge