Zhengwei Xie
PolarMem: A Training-Free Polarized Latent Graph Memory for Verifiable Multimodal Agents
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:As multimodal agents evolve from passive observers to long-horizon decision-makers, they require memory systems that provide not just information availability but logical verifiability. A fundamental limitation of current architectures is the epistemic asymmetry inherent in probabilistic vision-language models and dense associative memories: they conflate semantic affinity with factual existence and structurally fail to encode negative constraints. To this end, we introduce PolarMem, a training-free Polarized Latent Graph Memory designed to ground agent reasoning in verifiable evidence. PolarMem transforms fuzzy perceptual likelihoods into discrete logical constraints through non-parametric distributional partitioning. Furthermore, it employs a polarized graph topology with orthogonal inhibitory connections to explicitly store verified negation as a primary cognitive state. At inference time, we enforce a logic-dominant retrieval paradigm, suppressing hallucinatory patterns that violate negative constraints. Extensive evaluation across eight frozen Vision--Language Models and six benchmarks demonstrates that PolarMem functions as a robust cognitive system, establishing a foundation for verifiable multimodal agents. Our code is available at https://github.com/czs-ict/PolarMem.
Prediction and optimization of NaV1.7 inhibitors based on machine learning methods
Nov 29, 2019
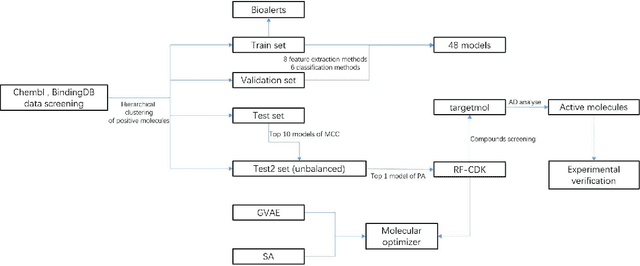


Abstract:Objectives NaV1.7 is a key target related to pain. This study focused on predicting and optimizing inhibitors of NaV1.7 using machine learning methods, and using patch-clamp methods to validate them at the cellular level. Materials and Methods We used Chembl, BindingDB, and data from the literature to establish classification models for inhibitors. The imbalanced data set test2 was used to screen the best-performing model to screen commercial compound libraries, and whole-cell voltage-clamp was used to validate inhibitors. We propose a molecular group optimization method using a combination of Grammer Variational Autoencoder, classification model, and simulated annealing algorithm. Results and Conclusion We get the model RF-CDK that performs best in the imbalanced data set. Of the three compounds that may have inhibitory effects, Nortriptyline has been experimentally verified. In the molecular optimization method, the best result of the optimization results of CHEMBL2325245 is MS = 1.052, PROB = 0.527, SA = 2.587, QED = 0.462. 40 molecules located in the applicability domain of RF-CDK were used for optimization, among which 34 molecules gave larger MS values.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge