Zhengbao JIang
DocCoder: Generating Code by Retrieving and Reading Docs
Jul 13, 2022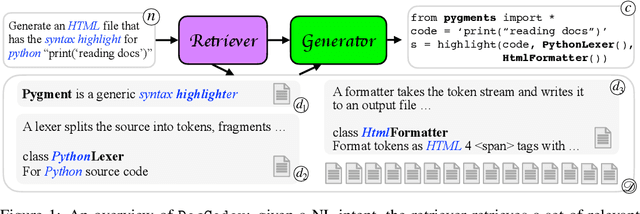
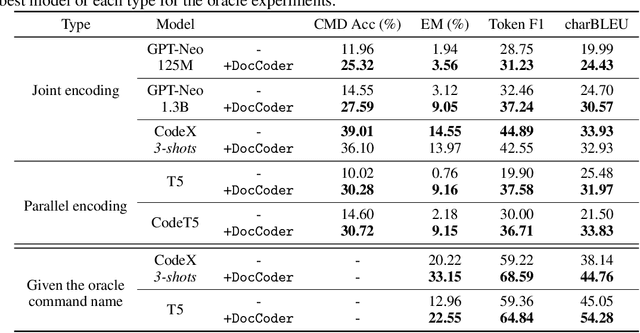
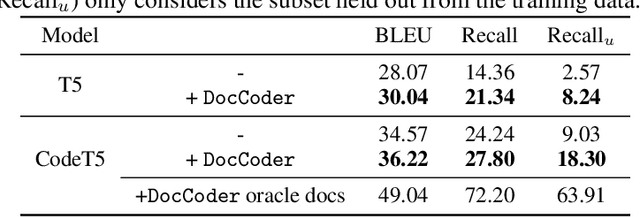
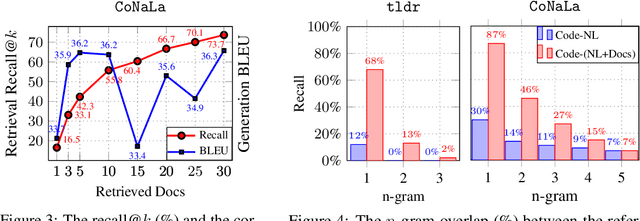
Abstract:Natural-language-to-code models learn to generate a code snippet given a natural language (NL) intent. However, the rapid growth of both publicly available and proprietary libraries and functions makes it impossible to cover all APIs using training examples, as new libraries and functions are introduced daily. Thus, existing models inherently cannot generalize to using unseen functions and libraries merely through incorporating them into the training data. In contrast, when human programmers write programs, they frequently refer to textual resources such as code manuals, documentation, and tutorials, to explore and understand available library functionality. Inspired by this observation, we introduce DocCoder: an approach that explicitly leverages code manuals and documentation by (1) retrieving the relevant documentation given the NL intent, and (2) generating the code based on the NL intent and the retrieved documentation. Our approach is general, can be applied to any programming language, and is agnostic to the underlying neural model. We demonstrate that DocCoder consistently improves NL-to-code models: DocCoder achieves 11x higher exact match accuracy than strong baselines on a new Bash dataset tldr; on the popular Python CoNaLa benchmark, DocCoder improves over strong baselines by 1.65 BLEU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge