Zhenan Feng
Graph Neural Network and Superpixel Based Brain Tissue Segmentation (Corrected Version)
Sep 21, 2022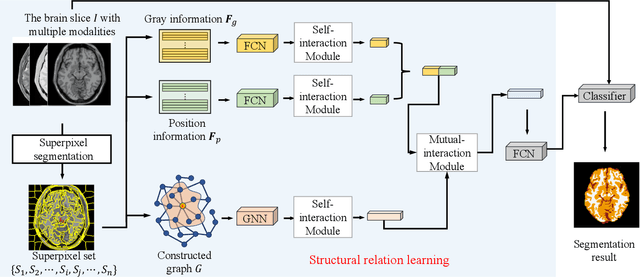
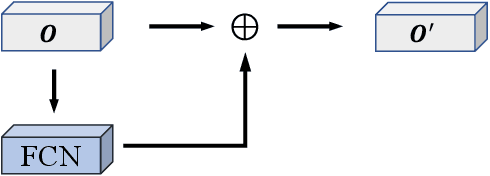
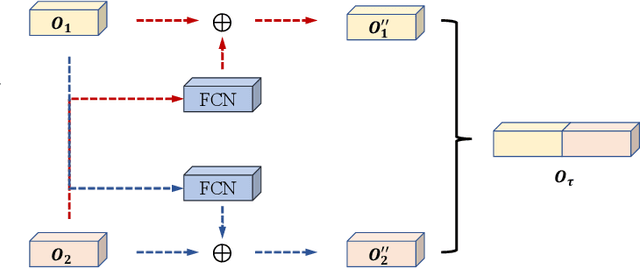
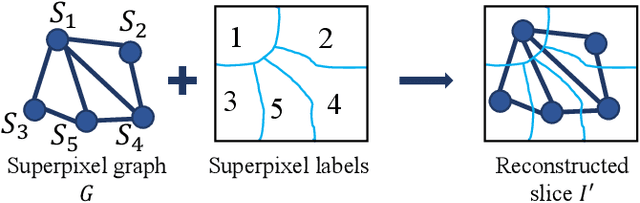
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are usually used as a backbone to design methods in biomedical image segmentation. However, the limitation of receptive field and large number of parameters limit the performance of these methods. In this paper, we propose a graph neural network (GNN) based method named GNN-SEG for the segmentation of brain tissues. Different to conventional CNN based methods, GNN-SEG takes superpixels as basic processing units and uses GNNs to learn the structure of brain tissues. Besides, inspired by the interaction mechanism in biological vision systems, we propose two kinds of interaction modules for feature enhancement and integration. In the experiments, we compared GNN-SEG with state-of-the-art CNN based methods on four datasets of brain magnetic resonance images. The experimental results show the superiority of GNN-SEG.
Prototyping Virtual Reality Serious Games for Building Earthquake Preparedness: The Auckland City Hospital Case Study
Feb 26, 2018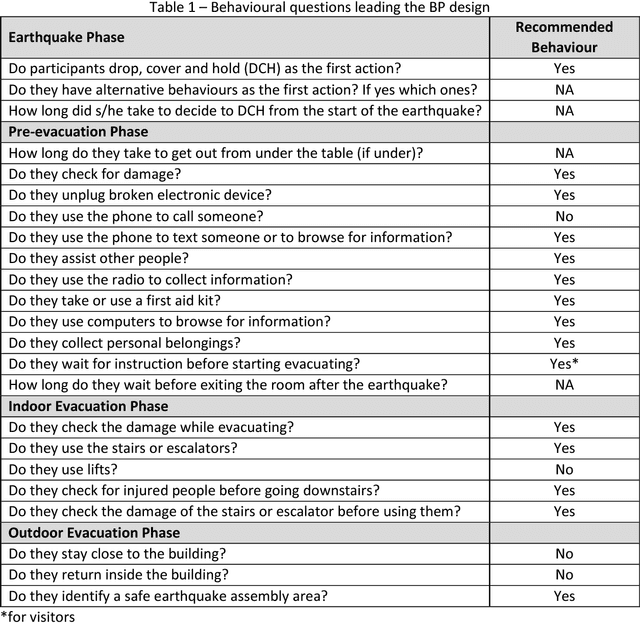
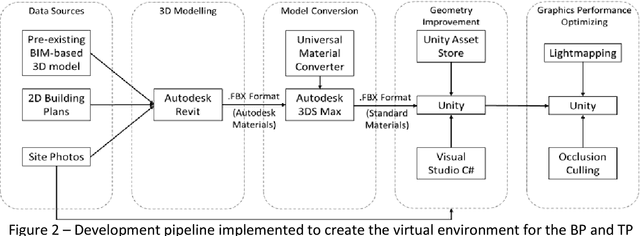
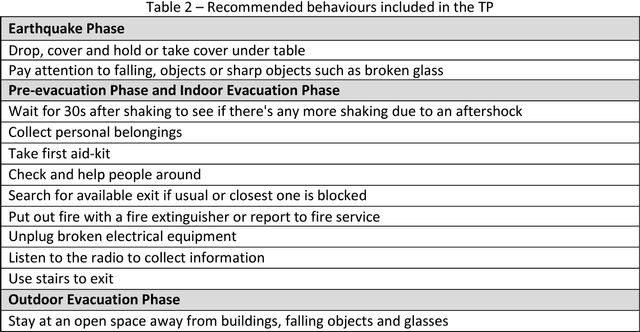
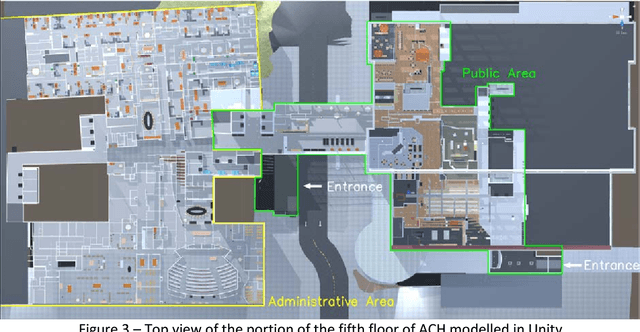
Abstract:Enhancing evacuee safety is a key factor in reducing the number of injuries and deaths that result from earthquakes. One way this can be achieved is by training occupants. Virtual Reality (VR) and Serious Games (SGs), represent novel techniques that may overcome the limitations of traditional training approaches. VR and SGs have been examined in the fire emergency context, however, their application to earthquake preparedness has not yet been extensively examined. We provide a theoretical discussion of the advantages and limitations of using VR SGs to investigate how building occupants behave during earthquake evacuations and to train building occupants to cope with such emergencies. We explore key design components for developing a VR SG framework: (a) what features constitute an earthquake event, (b) which building types can be selected and represented within the VR environment, (c) how damage to the building can be determined and represented, (d) how non-player characters (NPC) can be designed, and (e) what level of interaction there can be between NPC and the human participants. We illustrate the above by presenting the Auckland City Hospital, New Zealand as a case study, and propose a possible VR SG training tool to enhance earthquake preparedness in public buildings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge